A Critical Role of the IL-22-IL-22 Binding Protein Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 36551508
- PMCID: PMC9775560
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14246019
A Critical Role of the IL-22-IL-22 Binding Protein Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
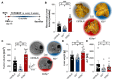
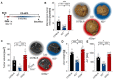
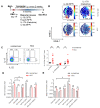
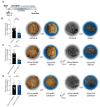
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks among the five most common cancer entities worldwide and leads to hundred-thousands of deaths every year. Despite some groundbreaking therapeutical revelations during the last years, the overall prognosis remains poor. Although the immune system fights malignant transformations with a robust anti-tumor response, certain immune mediators have also been shown to promote cancer development. For example, interleukin (IL)-22 has been associated with HCC progression and worsened prognosis in multiple studies. However, the underlying mechanisms of the pathological role of IL-22-signaling as well as the role of its natural antagonist IL-22 binding protein (IL-22BP) in HCC remain elusive. Here, we corroborate the pathogenic role of IL-22 in HCC by taking advantage of two mouse models. Moreover, we observed a protective role of IL-22BP during liver carcinogenesis. While IL-22 was mainly produced by CD4+ T cells in HCC, IL-22BP was abundantly expressed by neutrophils during liver carcinogenesis. Hepatocytes could be identified as a major target of this pathological IL-22-signaling. Moreover, abrogation of IL-22 signaling in hepatocytes in IL22ra1flox/flox × AlbCre+ mice reduced STEAP4 expression-a known oncogene-in HCC in vivo. Likewise, STEAP4 expression correlated with IL22 levels in human HCC samples, but not in healthy liver specimens. In conclusion, these data encourage the development of therapeutical approaches that target the IL-22-IL-22BP axis in HCC.
Keywords: IL-22; IL-22BP; Th22; hepatocellular carcinoma; neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The good and the bad about separation anxiety: roles of IL-22 and IL-22BP in liver pathologies.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Aug;43(4):591-607. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00854-z. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33851257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17 signaling in steatotic hepatocytes and macrophages promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in alcohol-related liver disease.J Hepatol. 2020 May;72(5):946-959. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.12.016. Epub 2019 Dec 31. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31899206 Free PMC article.
-
IL-22BP controls the progression of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 May 31;13:1170502. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1170502. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37324022 Free PMC article.
-
SPTBN1 inhibits inflammatory responses and hepatocarcinogenesis via the stabilization of SOCS1 and downregulation of p65 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Theranostics. 2021 Feb 20;11(9):4232-4250. doi: 10.7150/thno.49819. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754058 Free PMC article.
-
IL-22 Binding Protein (IL-22BP) in the Regulation of IL-22 Biology.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 16;12:766586. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.766586. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of TLR4 in the Immunotherapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Can We Teach an Old Dog New Tricks?Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 17;15(10):2795. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102795. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes-Mediated STEAP4 Enhances Retinal Oxidative Stress and Impacts the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;14(2):205. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020205. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002391 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional roles of inflammation and its causative factors in primary liver cancer: A literature review.World J Hepatol. 2023 Dec 27;15(12):1258-1271. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1258. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 38223416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-22+ CD4+ subset in patients with hepatitis C virus and correlation with clinical factor.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Feb 25;13(1):43-52. doi: 10.62347/DMJC6311. eCollection 2024. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38496355 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL-22 in cancer.Med Oncol. 2024 Sep 5;41(10):240. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02481-8. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39231878 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

