Immunohistochemical Markers of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Are Related to Extensive Lymph Nodal Spread, Peritoneal Dissemination, and Poor Prognosis in the Microsatellite-Stable Diffuse Histotype of Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 36551509
- PMCID: PMC9776345
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14246023
Immunohistochemical Markers of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Are Related to Extensive Lymph Nodal Spread, Peritoneal Dissemination, and Poor Prognosis in the Microsatellite-Stable Diffuse Histotype of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
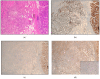
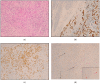
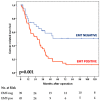
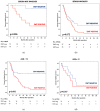
Background: Although the prognostic value of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in gastric cancer has been reported in several studies, the strong association with the diffuse type may represent a confounding factor. Our aim is to investigate potential correlations among EMT status, tumor advancement, and prognosis in diffuse gastric cancer. Methods: Between 1997 and 2012, 84 patients with microsatellite-stable (MSS) diffuse-type tumors underwent surgery. The EMT phenotype was assessed with the E-cadherin, CD44, and zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB-1) immunohistochemical markers. Results: Forty-five out of 84 cases (54%) were EMT-positive; more advanced nodal status (p = 0.010), pTNM stage (p = 0.032), and vascular invasion (p = 0.037) were observed in this group. The median numbers of positive nodes (13 vs. 5) and involved nodal stations (4 vs. 2) were higher in the EMT-positive group. The cancer-related survival time was 26 months in EMT-positive cases vs. 51 in negative cases, with five-year survival rates of 17% vs. 51%, respectively (p = 0.001). The EMT status had an impact on the prognosis of patients with <70 years, R0 resections, or treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy. Tumor relapses after surgery and peritoneal spread were significantly higher in the EMT-positive tumors. Conclusions: EMT status, when assessed through immunohistochemistry, identified an aggressive phenotype of MSS diffuse-type tumors with extensive lymph nodal spread, peritoneal dissemination, and worse long-term outcomes.
Keywords: diffuse histotype; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; gastric cancer; immunohistochemistry; microsatellite-stable tumors; outcome; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition predicts prognosis in clinical gastric cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2014 Jun;109(7):684-9. doi: 10.1002/jso.23564. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24453058
-
Clinical significance of altering epithelial-mesenchymal transition in metastatic lymph nodes of gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2017 Sep;20(5):802-810. doi: 10.1007/s10120-017-0705-x. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Gastric Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28247164
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition predicts prognosis of pancreatic cancer.Surgery. 2013 Nov;154(5):946-54. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.05.004. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Surgery. 2013. PMID: 24075276
-
The EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal-transition)-related protein expression indicates the metastatic status and prognosis in patients with ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2014 Jul 27;7:76. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-7-76. J Ovarian Res. 2014. PMID: 25296567 Free PMC article.
-
The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.Pathology. 2007 Jun;39(3):305-18. doi: 10.1080/00313020701329914. Pathology. 2007. PMID: 17558857 Review.
Cited by
-
EZH2: An Accomplice of Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;15(2):425. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020425. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical implications of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancers which potentially spread to peritoneum.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Jul;27(7):2838-2851. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03837-2. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39775727 Review.
-
Posterior and Para-Aortic (D2plus) Lymphadenectomy after Neoadjuvant/Conversion Therapy for Locally Advanced/Oligometastatic Gastric Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 31;16(7):1376. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071376. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611054 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of the prognostic nomogram model for patients with diffuse-type gastric cancer based on the SEER database.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;15(1):305. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01180-0. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39048774 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Biology of Cancer Peritoneal Metastasis: Multiclonal Seeding and Peritoneal Tumor Microenvironment.Cancer Sci. 2025 May;116(5):1171-1180. doi: 10.1111/cas.70021. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 39948828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koemans W.J., Lurvink R.J., Grootscholten C., Verhoeven R.H.A., de Hingh I.H., van Sandick J.W. Synchronous peritoneal metastases of gastric cancer origin: Incidence, treatment and survival of a nationwide Dutch cohort. Gastric Cancer. 2021;24:800–809. doi: 10.1007/s10120-021-01160-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marrelli D., Morgagni P., De Manzoni G., Marchet A., Baiocchi G.L., Giacopuzzi S., Coniglio A., Mocellin S., Saragoni L., Roviello F. External Validation of a Score Predictive of Recurrence after Radical Surgery for Non-Cardia Gastric Cancer: Results of a Follow-Up Study. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015;221:280–290. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.03.042. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

