Pharmacological Optimization of PSMA-Based Radioligand Therapy
- PMID: 36551776
- PMCID: PMC9775864
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10123020
Pharmacological Optimization of PSMA-Based Radioligand Therapy
Abstract
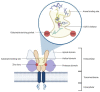
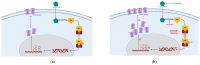
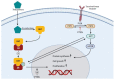
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common malignancy in men of middle and older age. The standard treatment strategy for PCa ranges from active surveillance in low-grade, localized PCa to radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, hormonal treatment and chemotherapy. Recently, the use of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radioligand therapy (RLT) for metastatic castration-resistant PCa has been approved. PSMA is predominantly, but not exclusively, expressed on PCa cells. Because of its high expression in PCa, PSMA is a promising target for diagnostics and therapy. To understand the currently used RLT, knowledge about pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of the PSMA ligand and the PSMA protein itself is crucial. PK and PD properties of the ligand and its target determine the duration and extent of the effect. Knowledge on the concentration-time profile, the target affinity and target abundance may help to predict the effect of RLT. Increased specific binding of radioligands to PSMA on PCa cells may be associated with better treatment response, where nonspecific binding may increase the risk of toxicity in healthy organs. Optimization of the radioligand, as well as synergistic effects of concomitant agents and an improved dosing strategy, may lead to more individualized treatment and better overall survival.
Keywords: PSMA; lutetium; optimization; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; prostate cancer; radioligand; theranostics; therapy; variability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
177 Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Initial 254-patient results from a prospective registry (REALITY Study).Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Feb;49(3):1075-1085. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05525-7. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34494131 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of [177Lu]-PSMA-I&T Radioligand Therapy in Octogenarians with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Report on 80 Patients over the Age of 80 Years.J Nucl Med. 2023 Aug;64(8):1244-1251. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.265259. Epub 2023 Jun 15. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37321824
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
Theranostics for Advanced Prostate Cancer: Current Indications and Future Developments.Eur Urol Oncol. 2019 Mar;2(2):152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Eur Urol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31017091 Review.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Effectiveness and Toxicities of Lutetium-177-labeled Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen-targeted Radioligand Therapy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol. 2021 Jul;80(1):82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.03.004. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 33840558 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Nuclear Medicine Therapeutics Targeting PSMA among Alpha-Emitting Nuclides.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 11;25(2):933. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020933. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256007 Free PMC article.
-
From Despair to Hope: First Arabic Experience of 177Lu-PSMA and 161Tb-PSMA Therapy for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 23;16(11):1974. doi: 10.3390/cancers16111974. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893095 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of biochemical PSA dynamics after radioligand therapy with [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-I&T using a population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.EJNMMI Phys. 2024 Apr 24;11(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40658-024-00642-2. EJNMMI Phys. 2024. PMID: 38656678 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Labeled Small Peptides in Cancer Imaging and Fluorescence-Guided Surgery: Progress and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 22;18(2):143. doi: 10.3390/ph18020143. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40005958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostate Cancer: From Molecular Imaging to Immunological and Target Therapies.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 14;11(4):1176. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041176. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration FDA Approves Pluvicto for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. [(accessed on 26 October 2022)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-appro....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

