The Functional Properties and Physiological Roles of Signal-Transducing Adaptor Protein-2 in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory and Immune Disorders
- PMID: 36551835
- PMCID: PMC9776019
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10123079
The Functional Properties and Physiological Roles of Signal-Transducing Adaptor Protein-2 in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory and Immune Disorders
Abstract
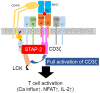
Adaptor molecules play a crucial role in signal transduction in immune cells. Several adaptor molecules, such as the linker for the activation of T cells (LAT) and SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa (SLP-76), are essential for T cell development and activation following T cell receptor (TCR) aggregation, suggesting that adaptor molecules are good therapeutic targets for T cell-mediated immune disorders, such as autoimmune diseases and allergies. Signal-transducing adaptor protein (STAP)-2 is a member of the STAP family of adaptor proteins. STAP-2 functions as a scaffold for various intracellular proteins, including BRK, signal transducer, and activator of transcription (STAT)3, STAT5, and myeloid differentiation primary response protein (MyD88). In T cells, STAP-2 is involved in stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α-induced migration, integrin-dependent cell adhesion, and Fas-mediated apoptosis. We previously reported the critical function of STAP-2 in TCR-mediated T cell activation and T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Here, we review how STAP-2 affects the pathogenesis of T cell-mediated inflammation and immune diseases in order to develop novel STAP-2-targeting therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: T cell antigen receptor (TCR); T cells; immune response; signal transduction; signal-transducing adaptor protein-2 (STAP-2).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

