Secondary Terpenes in Cannabis sativa L.: Synthesis and Synergy
- PMID: 36551898
- PMCID: PMC9775512
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10123142
Secondary Terpenes in Cannabis sativa L.: Synthesis and Synergy
Abstract
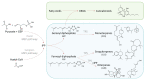
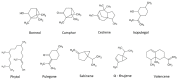
Cannabis is a complex biosynthetic plant, with a long history of medicinal use. While cannabinoids have received the majority of the attention for their psychoactive and pharmacological activities, cannabis produces a diverse array of phytochemicals, such as terpenes. These compounds are known to play a role in the aroma and flavor of cannabis but are potent biologically active molecules that exert effects on infectious as well as chronic diseases. Furthermore, terpenes have the potential to play important roles, such as synergistic and/or entourage compounds that modulate the activity of the cannabinoids. This review highlights the diversity and bioactivities of terpenes in cannabis, especially minor or secondary terpenes that are less concentrated in cannabis on a by-mass basis. We also explore the question of the entourage effect in cannabis, which studies to date have supported or refuted the concept of synergy in cannabis, and where synergy experimentation is headed, to better understand the interplay between phytochemicals within Cannabis sativa L.
Keywords: biosynthesis; cannabinoids; cannabis; entourage effect; phytochemistry; synergy; terpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Entourage Effect and Analytical Chemistry: Chromatography as a Tool in the Analysis of the Secondary Metabolism of Cannabis sativa L.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(6):394-406. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221103093542. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 36330630 Review.
-
The Neurotherapeutic Arsenal in Cannabis sativa: Insights into Anti-Neuroinflammatory and Neuroprotective Activity and Potential Entourage Effects.Molecules. 2024 Jan 15;29(2):410. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020410. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabis Phytomolecule 'Entourage': From Domestication to Medical Use.Trends Plant Sci. 2020 Oct;25(10):976-984. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.04.007. Epub 2020 May 13. Trends Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32417167 Review.
-
Medicinal Properties of Cannabinoids, Terpenes, and Flavonoids in Cannabis, and Benefits in Migraine, Headache, and Pain: An Update on Current Evidence and Cannabis Science.Headache. 2018 Jul;58(7):1139-1186. doi: 10.1111/head.13345. Headache. 2018. PMID: 30152161 Review.
-
The Terroir of Cannabis: Terpene Metabolomics as a Tool to Understand Cannabis sativa Selections.Planta Med. 2019 Jul;85(9-10):781-796. doi: 10.1055/a-0915-2550. Epub 2019 May 16. Planta Med. 2019. PMID: 31096276
Cited by
-
Extraction of Cannabinoids and Terpenes from Hemp Flowers and Leaves (Cannabis sativa L., Futura 75): Chemical Profiling and Evaluation of Anticancer Properties.Molecules. 2025 Mar 15;30(6):1325. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061325. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40142100 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal and mycotoxin contaminants in cannabis and hemp flowers: implications for consumer health and directions for further research.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1278189. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1278189. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37928692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Special Issue: Therapeutic Potential for Cannabis and Cannabinoids.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 14;11(3):902. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030902. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979881 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hemp Extraction Procedures on Cannabinoid and Terpenoid Composition.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;13(16):2222. doi: 10.3390/plants13162222. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204658 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of the Anti-Parasitic Effect of a Cannabis sativa full-spectrum Extract on Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto.Acta Parasitol. 2025 Jul 14;70(4):157. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01090-3. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40659847
References
-
- Ranade A., Tavhare S.D., Acharya R., Pawar S.D. Cannabis (Bhanga) in Classical Text of Ayurveda: An Evidence-Based Rationale. In: Agrawal D.C., Kumar R., Dhanasekaran M., editors. Cannabis/Marijuana for Healthcare. Springer Nature; Singapore: 2022. pp. 235–251.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

