Three-Dimensional Digital Light-Processing Bioprinting Using Silk Fibroin-Based Bio-Ink: Recent Advancements in Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 36551978
- PMCID: PMC9775525
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10123224
Three-Dimensional Digital Light-Processing Bioprinting Using Silk Fibroin-Based Bio-Ink: Recent Advancements in Biomedical Applications
Abstract
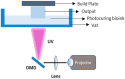
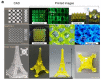
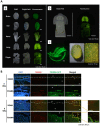
Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting has been developed as a viable method for fabricating functional tissues and organs by precisely spatially arranging biomaterials, cells, and biochemical components in a layer-by-layer fashion. Among the various bioprinting strategies, digital light-processing (DLP) printing has gained enormous attention due to its applications in tissue engineering and biomedical fields. It allows for high spatial resolution and the rapid printing of complex structures. Although bio-ink is a critical aspect of 3D bioprinting, only a few bio-inks have been used for DLP bioprinting in contrast to the number of bio-inks employed for other bioprinters. Recently, silk fibroin (SF), as a natural bio-ink material used for DLP 3D bioprinting, has gained extensive attention with respect to biomedical applications due to its biocompatibility and mechanical properties. This review introduces DLP-based 3D bioprinting, its related technology, and the fabrication process of silk fibroin-based bio-ink. Then, we summarize the applications of DLP 3D bioprinting based on SF-based bio-ink in the tissue engineering and biomedical fields. We also discuss the current limitations and future perspectives of DLP 3D bioprinting using SF-based bio-ink.
Keywords: bio-ink; biomedical application; digital light processing; silk fibroin; three-dimensional bioprinting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- NRF-2020R1A2C3010040/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP)
- HI21C1847/Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI)
- NRF-2022R1I1A1A01071825/Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- None/Hallym University research fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

