Unmet Need for Oral Corticosteroids Use and Exacerbations of Asthma in Primary Care in Taiwan
- PMID: 36552009
- PMCID: PMC9775049
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10123253
Unmet Need for Oral Corticosteroids Use and Exacerbations of Asthma in Primary Care in Taiwan
Abstract
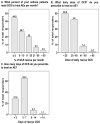
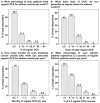
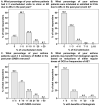
Patients with asthma are treated in primary healthcare facilities (PHCFs) in Taiwan, where the asthma control status associated with acute exacerbation (AE) and use of oral corticosteroids (OCS) and short-acting β2-agonist (SABA) inhalers remains unclear. A cross-sectional, close-ended, face-to-face questionnaire survey invited board-certified physicians who treat adult asthma patients in PHCFs. The contents of the questionnaire included three parts: rescue OCS to treat AE, regular OCS for asthma control, and AE-related adverse outcomes. There were 445 out of 500 physicians who completed the questionnaire, with 61% of them being non-pulmonologists. A substantial proportion of asthma patients needed rescue OCS or regular OCS each month, or ≥3 canisters of SABA inhalers per year. Approximately 86% of physicians reported their patients with ≥2 AE-related unscheduled visits to clinics or emergency departments in the past year. A total of 41% of physicians reported their patients receiving intubation or intensive care in the past year. A total of 92% of physicians prescribed rescue OCS ≤ 40 mg/day. A total of 92% of physicians prescribed rescue OCS for a duration of ≤7 days for AEs. A total of 85% of physicians prescribed regular OCS ≤ 10 mg/day for asthma control. This is the first study to present the perceptions of asthma-treating physicians on the use of OCS in PHCFs. In summary, 31% of physicians reported ≥ 6% of their patients needed OCS for asthma control and 41% of physicians reported their patients with adverse outcomes in the past year. Thus, the need to improve asthma control in Taiwan is suggested by our study results.
Keywords: exacerbation; oral corticosteroid; primary healthcare facility; severe asthma; short-acting β2-agonist.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-acting β2-agonist prescription patterns in patients with asthma in Turkey: results from SABINA III.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Jun 2;22(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02008-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35655251 Free PMC article.
-
Practice patterns for oral corticosteroid burst therapy in the outpatient management of acute asthma exacerbations.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012 Jan-Feb;33(1):82-9. doi: 10.2500/aap.2012.33.3499. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012. PMID: 22183118
-
Short-Acting Beta-2-Agonist Exposure and Severe Asthma Exacerbations: SABINA Findings From Europe and North America.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Sep;10(9):2297-2309.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.02.047. Epub 2022 Mar 29. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35364341
-
Severe asthma: oral corticosteroid alternatives and the need for optimal referral pathways.J Asthma. 2021 Apr;58(4):448-458. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2019.1705335. Epub 2020 Jan 11. J Asthma. 2021. PMID: 31928102 Review.
-
Omalizumab as alternative to chronic use of oral corticosteroids in severe asthma.Respir Med. 2019 Apr;150:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 30961951 Review.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Updated 2019. [(accessed on 1 June 2019)]. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-J....
-
- Sweeney J., Patterson C.C., Menzies-Gow A., Niven R.M., Mansur A.H., Bucknall C., Chaudhuri R., Price D., Brightling C.E., Heaney L.G., et al. Comorbidity in severe asthma requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy: Cross-sectional data from the Optimum Patient Care Research Database and the British Thoracic Difficult Asthma Registry. Thorax. 2016;71:339–346. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207630. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chou C.L., Perng D.W., Lin T.L., Lin A.M., Chen T.J., Wu M.S., Chou Y.C. Analysis of prescription pattern and guideline adherence in the management of asthma among medical institutions and physician specialties in Taiwan between 2000 and 2010. Clin. Ther. 2015;37:2275–2285. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.07.024. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

