Electroacupuncture Alleviates Neuroinflammation by Inhibiting the HMGB1 Signaling Pathway in Rats with Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy
- PMID: 36552192
- PMCID: PMC9776077
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12121732
Electroacupuncture Alleviates Neuroinflammation by Inhibiting the HMGB1 Signaling Pathway in Rats with Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy
Abstract
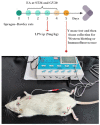
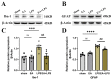
Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy (SAE) is common in sepsis patients, with high mortality rates. It is believed that neuroinflammation is an important mechanism involved in SAE. High mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1), as a late pro-inflammatory factor, is significantly increased during sepsis in different brain regions, including the hippocampus. HMGB1 causes neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment through direct binding to advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Electroacupuncture (EA) at Baihui (GV20) and Zusanli (ST36) is beneficial for neurological diseases and experimental sepsis. Our study used EA to treat SAE induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in male Sprague-Dawley rats. The Y maze test was performed to assess working memory. Immunofluorescence (IF) and Western blotting (WB) were used to determine neuroinflammation and the HMGB1 signaling pathway. Results showed that EA could improve working memory impairment in rats with SAE. EA alleviated neuroinflammation by downregulating the hippocampus's HMGB1/TLR4 and HMGB1/RAGE signaling, reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory factors, and relieving microglial and astrocyte activation. However, EA did not affect the tight junctions' expression of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the hippocampus.
Keywords: HMGB1; electroacupuncture; neuroinflammation; sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao L., An R., Yang Y., Yang X., Liu H., Yue L., Li X., Lin Y., Reiter R.J., Qu Y. Melatonin alleviates brain injury in mice subjected to cecal ligation and puncture via attenuating inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress: The role of SIRT1 signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2015;59:230–239. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12254. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

