Porcine Interleukin-17 and 22 Co-Expressed by Yarrowia lipolytica Enhance Immunity and Increase Protection against Bacterial Challenge in Mice and Piglets
- PMID: 36552257
- PMCID: PMC9774966
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11121747
Porcine Interleukin-17 and 22 Co-Expressed by Yarrowia lipolytica Enhance Immunity and Increase Protection against Bacterial Challenge in Mice and Piglets
Abstract
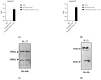
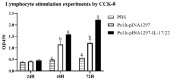
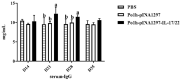
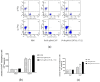
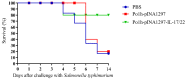
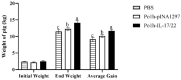
Drug resistance in economic animals to pathogens is a matter of widespread concern due to abuse of antibiotics. In order to develop a safe and economical immunopotentiator to raise the immunity and antibacterial response as a replacement for antibiotics, a recombinant yeast co-expressing pig interleukin-17 (IL-17) and IL-22 was constructed and designated as Po1h-pINA1297-IL-17/22. To evaluate the immunoregulator activities of Po1h-pINA1297-IL-17/22, two experiment groups (oral inoculation with Po1h-pINA1297 or Po1h-pINA1297-IL-17/22) and a negative control group (PBS) were set up using 4-week-old female BALB/c mice (10/group). The level of cytokines, including IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, and IFN-γ, were detected by ELISA, and the circulating CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes were quantified by flow cytometry. The IgG and secretory IgA (SIgA) levels in both small intestine and fecal matter were also measured by ELISA. The results indicated that the IgG antibody titer and SIgA concentration increased significantly in the Po1h-pINA1297-IL17/22 group in comparison with the controls (p < 0.05) and so did the cytokine levels in the serum (IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, and IFN-γ). In addition, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were also obviously elevated in the Po1h-pINA1297-IL17/22 group on 35th day (p < 0.05). After challenge with pathogenic Salmonella typhimurium, the Po1h-pINA1297-IL17/22 group showed a relatively higher survival rate without obvious infectious symptoms. On the contrary, the mortality of control group reached 80% due to bacterial infection. As for the piglet experiment, 30 healthy 7-day piglets were similarly attributed into three groups. The oral inoculation of piglets with Po1h-pINA1297-IL17/22 also markedly improved the growth performance and systemic immunity (up-regulations of IL-4, IL-6, IL-15, IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23). Overall, the results indicated that Po1h-pINA1297-IL17/22 effectively promoted the humoral and cellular immunity against bacterial infection. These proved the promising potential of Po1h-pINA1297-IL-17/22 to be a potent immunopotentiator for the prevention of microbial pathogen infections.
Keywords: Yarrowia lipolytica; bacterial infection; immunity; immunopotentiator; interleukin-22; pig interleukin-17.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

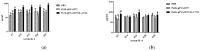
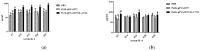
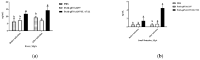


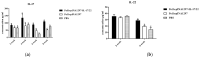
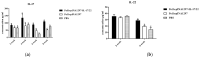

Similar articles
-
Enhanced Immunity and Infection Resistance in Mice Through Co-Expression of Porcine IL-3, IL-7, and IL-15 Fusion Molecules in Yarrowia lipolytica.Biology (Basel). 2025 Apr 2;14(4):366. doi: 10.3390/biology14040366. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282231 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of phytase gene phyA in Yarrowia lipolytica po1h].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2010 May;26(5):610-5. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20684304 Chinese.
-
Enhancement of Immune Response and Anti-Infection of Mice by Porcine Antimicrobial Peptides and Interleukin-4/6 Fusion Gene Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;8(3):552. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030552. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967351 Free PMC article.
-
Overproduction of pro-transglutaminase from Streptomyces hygroscopicus in Yarrowia lipolytica and its biochemical characterization.BMC Biotechnol. 2015 Aug 14;15:75. doi: 10.1186/s12896-015-0193-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26272462 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted immune responses and protective efficacy elicited by a recombinant autolyzed Salmonella expressing FliC flagellar antigen of F18+Escherichia coli.Vaccine. 2016 Dec 7;34(50):6335-6342. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.10.066. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27817960
References
-
- Agyare C., Boamah V.E., Zumbi C.N., Osei F.B. Antibiotic use in poultry production and its effects on bacterial resistance. In: Kumar Y., editor. Antimicrobial Resistance—A Global Threat. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2018. pp. 33–51.
Grants and funding
- 2011DFA10101103/National International Cooperation Program,
- 30871855/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020YFH0020, 2021YFYZ0030/Scientific projects of Sichuan province
- XYZS2021-02/The Open Project of New Drug Pre-production Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province
- 19Z06/Collaborative Innovation Center of Sichuan for Elderly Care and Health, Chengdu Medical College
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

