Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review
- PMID: 36552293
- PMCID: PMC9775288
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11121784
Complications of Severe Odontogenic Infections: A Review
Abstract
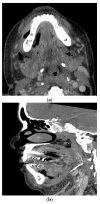
Severe odontogenic infections are routinely treated with little associated morbidity and mortality. Improvements in surgical techniques, antibiotic treatments, and imaging modalities have made associated complications exceedingly rare. A number of complications have been described in the literature including airway obstruction, descending necrotizing mediastinitis, orbital abscess, septic cavernous sinus thrombosis, cerebral abscess, sepsis, necrotizing fasciitis, and Lemierre's syndrome. The purpose of this article is to discuss the pathophysiology of severe odontogenic infections and the risk factors associated with the development of complications. Given the morbidity and mortality of these conditions, it is important to review the clinical features of each and the diagnostic tools that aid in early recognition.
Keywords: abscess; infection; odontogenic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

