Mesothelin Gene Variants Affect Soluble Mesothelin-Related Protein Levels in the Plasma of Asbestos-Exposed Males and Mesothelioma Patients from Germany
- PMID: 36552335
- PMCID: PMC9776112
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11121826
Mesothelin Gene Variants Affect Soluble Mesothelin-Related Protein Levels in the Plasma of Asbestos-Exposed Males and Mesothelioma Patients from Germany
Abstract
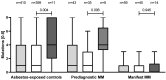
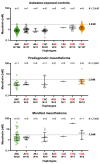
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is a severe disease mostly caused by asbestos exposure. Today, one of the best available biomarkers is the soluble mesothelin-related protein (SMRP), also known as mesothelin. Recent studies have shown that mesothelin levels are influenced by individual genetic variability. This study aimed to investigate the influence of three mesothelin (MSLN) gene variants (SNPs) in the 5′-untranslated promoter region (5′-UTR), MSLN rs2235503 C > A, rs3764246 A > G, rs3764247 A > C, and one (rs1057147 G > A) in the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of the MSLN gene on plasma concentrations of mesothelin in 410 asbestos-exposed males without cancer and 43 males with prediagnostic MM (i.e., with MM diagnosed later on) from the prospective MoMar study, as well as 59 males with manifest MM from Germany. The mesothelin concentration differed significantly between the different groups (p < 0.0001), but not between the prediagnostic and manifest MM groups (p = 0.502). Five to eight mutations of the four SNP variants studied were associated with increased mesothelin concentrations (p = 0.001). The highest mesothelin concentrations were observed for homozygous variants of the three promotor SNPs in the 5′-UTR (p < 0.001), and the highest odds ratio for an elevated mesothelin concentration was observed for MSLN rs2235503 C > A. The four studied SNPs had a clear influence on the mesothelin concentration in plasma. Hence, the analysis of these SNPs may help to elucidate the diagnostic background of patients displaying increased mesothelin levels and might help to reduce false-positive results when using mesothelin for MM screening in high-risk groups.
Keywords: MoMar cohort; asbestos; biomarker; blood test; confounder; manifest mesothelioma; mesothelin; prediagnostic mesothelioma; prospective study; variant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hassan R., Remaley A.T., Sampson M.L., Zhang J., Cox D.D., Pingpank J., Alexander R., Willingham M., Pastan I., Onda M. Detection and quantification of serum mesothelin, a tumour marker for patients with mesothelioma and ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:447–453. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1477. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

