Early Exposure to Environmental Pollutants: Imidacloprid Potentiates Cadmium Toxicity on Zebrafish Retinal Cells Death
- PMID: 36552404
- PMCID: PMC9774592
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12243484
Early Exposure to Environmental Pollutants: Imidacloprid Potentiates Cadmium Toxicity on Zebrafish Retinal Cells Death
Abstract
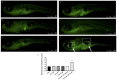
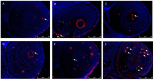
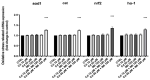
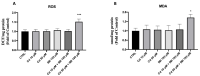
In the present study, we analyzed the combination of non-toxic concentrations per se, of Cd and a pesticide the imidacloprid (IMI) (10 and 50 μM for Cd and 195 μM for IMI), to highlight early developmental toxicity and possible damage to retinal cells. Co-exposure to Cd and IMI showed a toxic effect in zebrafish larval development, with lowered degrees of survival and hatching, and in some cases the induction of structural alterations and edema. In addition, co-exposure to 50 and 195 μM, respectively, for Cd and IMI, also showed increased apoptosis in eye cells, accompanied by up regulation of genes associated with antioxidant markers (cat, sod1, nrf2 and ho-1). Thus, the present study aims to highlight how the presence of multiple contaminants, even at low concentrations, can be a risk factor in a model of zebrafish (Danio rerio). The presence of other contaminants, such as IMI, can cause an enhancement of the toxic action of Cd on morphological changes in the early life stage of zebrafish, but more importantly disrupt the normal development of the retina, eventually triggering apoptosis.
Keywords: apoptosis; environment contaminant; pesticides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of combined stressors to cadmium and high temperature on antioxidant defense, apoptotic cell death, and DNA methylation in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos.Sci Total Environ. 2020 May 10;716:137130. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137130. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32045767
-
Low concentrations of imidacloprid exposure induced gut toxicity in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio).Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021 Mar;241:108972. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108972. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33418081
-
Joint toxic effects of triazophos and imidacloprid on zebrafish (Danio rerio).Environ Pollut. 2018 Apr;235:470-481. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.120. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Environ Pollut. 2018. PMID: 29316522
-
Prolonged darkness attenuates imidacloprid toxicity through the brain-gut-microbiome axis in zebrafish, Danio rerio.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Jul 10;881:163481. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163481. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37068676
-
Rapid Assessment of Ocular Toxicity from Environmental Contaminants Based on Visually Mediated Zebrafish Behavior Studies.Toxics. 2023 Aug 16;11(8):706. doi: 10.3390/toxics11080706. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37624211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Pesticide Vinclozolin Toxicity Exposure on Cardiac Oxidative Stress and Myocardial Damage.Toxics. 2023 May 23;11(6):473. doi: 10.3390/toxics11060473. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37368573 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal toxicity of heavy metals and its involvement in retinal pathology.Food Chem Toxicol. 2024 Jun;188:114685. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2024.114685. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38663763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Review of Increasing Animal Health Threat of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): Harms, Limitations, and Alternatives to Manage Their Toxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 20;24(14):11707. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411707. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of exposure to urinary and blood heavy metals with visual disability among U.S. adults in NHANES 2013-2018.Front Public Health. 2025 May 9;13:1583105. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1583105. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40416683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simon-Delso N., Amaral-Rogers V., Belzunces L.P., Bonmatin J.-M., Chagnon M., Downs C., Furlan L., Gibbons D.W., Giorio C., Girolami V. Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): Trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015;22:5–34. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3470-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayasaka D., Korenaga T., Suzuki K., Saito F., Sánchez-Bayo F., Goka K. Cumulative ecological impacts of two successive annual treatments of imidacloprid and fipronil on aquatic communities of paddy mesocosms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012;80:355–362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.04.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

