The Prevalence of Trichinella spiralis in Domestic Pigs in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36552472
- PMCID: PMC9774926
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12243553
The Prevalence of Trichinella spiralis in Domestic Pigs in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
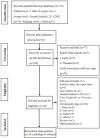
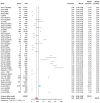
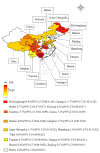
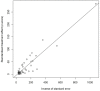
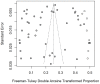
The meta-analysis was performed to assess the prevalence of T. spiralis in domestic pigs in China. The potential studies from seven databases (Pubmed, Web of science, Scopus, Google Scholar, CNKI, Wanfang, CBM) were searched. I2, Cochran's Q statistic and the funnel plot and Egger's test were used to assess heterogeneity and publication bias, respectively. In this study, a total of 179 articles were captured in the initially screened. Of these, we finally obtained 39 significant articles (including 43 studies involving in 551,097 pigs) for the final analysis. We calculated using a random-effects model, and we found the overall infection rate was 0.04 (95% CI 0.03-0.06). The highest prevalence region was Guangxi. The funnel plot and Egger's test showed no publication bias in our meta-analysis. In addition, this high heterogeneity index was suggestive of potential variations which could be due to regions, quality scores, detection methods, publication years, or samplings. These results indicated that T. spiralis were still prevalent in some areas in China. This highlights the need for an increased focus on implementing affordable, appropriate control programs to reduce economic losses and T. spiralis infection in domestic pigs in China.
Keywords: foodborne disease; parasitic disease; trichinellosis; zoonosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global prevalence of Porcine Astrovirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Prev Vet Med. 2025 May;238:106465. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2025.106465. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Prev Vet Med. 2025. PMID: 39954603
-
Effect of somatometric parameters on the prevalence and severity of varicocele: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Jan 20;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00695-3. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33472653 Free PMC article.
-
Low Economic Class Might Predispose Children under Five Years of Age to Stunting in Ethiopia: Updates of Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Nutr Metab. 2020 Dec 12;2020:2169847. doi: 10.1155/2020/2169847. eCollection 2020. J Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 33489361 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of depressive symptoms among nurses in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 7;15(7):e0235448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235448. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32634150 Free PMC article.
-
[The usefulness of ELISA test for early serological detection of Trichinella spp. infection in pigs].Wiad Parazytol. 2007;53(2):149-51. Wiad Parazytol. 2007. PMID: 17912813 Polish.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Anthelmintic Effect of Mexican Plant Extracts and Partitions Against Trichinella spiralis and Strongyloides venezuelensis.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;13(24):3484. doi: 10.3390/plants13243484. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacon R.T., Sofos J.N. Food Safety Handbook. John Wiley & Sons; New York, NY, USA: 2003. Characteristics of Biological Hazards in Foods; pp. 157–195.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

