Redox Status, Estrogen and Progesterone Production by Swine Granulosa Cells Are Impaired by Triclosan
- PMID: 36552479
- PMCID: PMC9774123
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12243559
Redox Status, Estrogen and Progesterone Production by Swine Granulosa Cells Are Impaired by Triclosan
Abstract
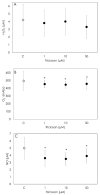
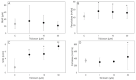
Triclosan is a chlorinated biphenolic with a broad spectrum of antiseptic activities used in cosmetics and hygiene products. Continuous exposure can lead to absorption and bioaccumulation of this substance with harmful health effects. In fact, previous studies have shown that Triclosan acts as an endocrine-disrupting chemical on reproductive organs, with consequent negative effects on reproductive physiology. Therefore, to assess potential adverse impacts on fertility, we tested Triclosan on swine granulosa cells, a model of endocrine reproductive cells. We examined its effects on the main features of granulosa cell functions such as cell growth (BrdU incorporation and ATP production) and steroidogenesis (17-β estradiol and progesterone secretion). Moreover, since oxidant−antioxidant balance plays a pivotal role in follicular function, redox status markers (superoxide, hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide production, enzymatic and non-enzymatic scavenging activity) were studied. Our results show that Triclosan significantly inhibits cell growth (p < 0.001), steroidogenesis (p < 0.001), superoxide and nitric oxide production (p < 0.001), while it increases (p < 0.05) enzymatic defense systems. Collectively, these data suggest a disruption of the main granulosa cell functions, i.e., proliferation and hormone production, as well as an imbalance in redox status. On these bases, we can speculate that Triclosan would impair granulosa cell functions, thus exerting negative effects on reproductive function. Further studies are needed to explore lower Triclosan concentrations and to unravel its mechanisms of action at gene level.
Keywords: cell proliferation; free radicals; ovary; oxidative stress; steroidogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alice E. Comment on “Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999−2000: A National Reconnaissance”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003;36:1202–1211. - PubMed
-
- Zhou X., Zhou S.B., Zhang Y., Shi L. Determination of triclosan in wastewater using solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography with ultra-violet detection; Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering; Beijing, China. 11–16 June 2009; pp. 1–4.
-
- Jagini S., Konda S., Bhagawan D., Himabindu V. Emerging contaminant (triclosan) identification and its treatment: A review. SN Appl. Sci. 2019;1:640. doi: 10.1007/s42452-019-0634-x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

