Feed Supplemented with Aronia melanocarpa (AM) Relieves the Oxidative Stress Caused by Ovulation in Peak Laying Hens and Increases the Content of Yolk Precursors
- PMID: 36552494
- PMCID: PMC9774901
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12243574
Feed Supplemented with Aronia melanocarpa (AM) Relieves the Oxidative Stress Caused by Ovulation in Peak Laying Hens and Increases the Content of Yolk Precursors
Abstract
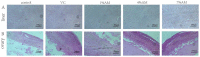
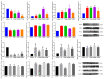
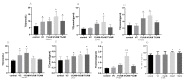
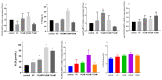
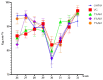
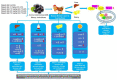
The continuous ovulation of laying hens during the peak period is likely to cause oxidative stress, resulting in a reduction in the laying cycle over time. The aim of this study was to evaluate the antioxidant effects of Aronia melanocarpa (AM) in the diet and its effect on the yolk precursor content caused by ovulation in laying hens during the peak period. A total of 300 25-week-old Roman brown laying hens were randomly divided into five groups with six replicates in each group, 10 in each replicate. The control group was fed a basal diet, the positive control group was fed a Vitamin C (VC) plus basal diet, and the experimental group was fed 1%, 4%, and 7% doses of AM plus diet according to the principle of energy and nitrogen requirements, which lasted eight weeks. At the end of the study, the egg quality, biochemical, and antioxidant markers, as well as mRNA and protein expressions, were evaluated to determine the potential signaling pathways involved. Results showed that the addition of AM to the feed increased the weight of laying hens at the peak of egg production and improved egg quality. The biochemical markers, as well as the antioxidant parameters in the serum, liver, and ovarian tissues, were ameliorated. The gene and protein expression of recombinant kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) in the liver and ovarian tissues was decreased, while nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression was increased. The feed supplemented with AM also increased the estrogen contents and lipid parameters, as well as the gene and protein expressions related to the yolk precursor. Feed supplemented with AM could improve the egg quality and the oxidative stress caused by the ovulation process of laying hens during the peak egg production period by activating the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. These results suggest that the feed supplemented with 1% AM and 4% AM can improve egg production in peak laying hens.
Keywords: Aronia melanocarpa; egg quality; oxidative stress; peak laying hens; yolk precursor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not declare a conflict of interest.
Figures
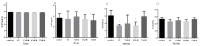

Similar articles
-
Effect of Selenium Source and Level on Performance, Egg Quality, Egg Selenium Content, and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Laying Hens.Foods. 2020 Jan 8;9(1):68. doi: 10.3390/foods9010068. Foods. 2020. PMID: 31936314 Free PMC article.
-
Flammulina velutipes stem regulates oxidative damage and synthesis of yolk precursors in aging laying hens by regulating the liver-blood-ovary axis.Poult Sci. 2023 Jan;102(1):102261. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102261. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36410067 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in egg yolk precursor formation of Guangxi Ma chickens with dissimilar laying rate at the same or various ages.Theriogenology. 2022 May;184:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.02.020. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Theriogenology. 2022. PMID: 35247786
-
Dietary arsenic supplementation induces oxidative stress by suppressing nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 in the livers and kidneys of laying hens.Poult Sci. 2021 Feb;100(2):982-992. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.11.061. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 33518152 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary supplementation of organic zinc on laying performance, egg quality and some biochemical parameters of laying hens.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018 Apr;102(2):e542-e549. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12793. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018. PMID: 28990706 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Dietary supplementation of coated sodium butyrate improves growth performance of laying ducks by regulating intestinal health and immunological performance.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1142915. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142915. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969242 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Aronia melanocarpa pomace improves the nutritive value of eggs, enhances ovarian function, and reshapes microbiota abundance in aged laying hens.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1422172. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1422172. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38962144 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary canthaxanthin improves egg production rate through regulating hepatic lipid metabolism and redox status in indigenous chickens.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jun 5;12:1607039. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1607039. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40538726 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid alleviates the negative effects of dexamethasone induced stress on production performance in Hyline Brown laying hens.Anim Nutr. 2024 Dec 14;20:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.11.011. eCollection 2025 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39949729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scappaticcio R., García J., Fondevila G., de Juan A.F., Cámara L., Mateos G.G. Influence of the energy and digestible lysine contents of the diet on performance and egg quality traits of brown-egg laying hens from 19 to 59 weeks of age. Poult. Sci. 2021;100:101211. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101211. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

