Recombinant Photolyase-Thymine Alleviated UVB-Induced Photodamage in Mice by Repairing CPD Photoproducts and Ameliorating Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 36552521
- PMCID: PMC9774824
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122312
Recombinant Photolyase-Thymine Alleviated UVB-Induced Photodamage in Mice by Repairing CPD Photoproducts and Ameliorating Oxidative Stress
Abstract
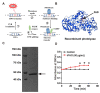
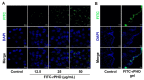
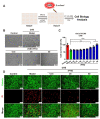
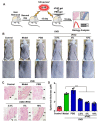
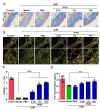
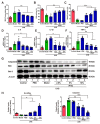
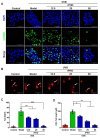
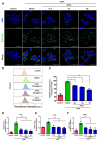
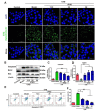
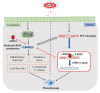
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) are the main mutagenic DNA photoproducts caused by ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation and represent the major cause of photoaging and skin carcinogenesis. CPD photolyase can efficiently and rapidly repair CPD products. Therefore, they are candidates for the prevention of photodamage. However, these photolyases are not present in placental mammals. In this study, we produced a recombinant photolyase-thymine (rPHO) from Thermus thermophilus (T. thermophilus). The rPHO displayed CPD photorepair activity. It prevented UVB-induced DNA damage by repairing CPD photoproducts to pyrimidine monomers. Furthermore, it inhibited UVB-induced ROS production, lipid peroxidation, inflammatory responses, and apoptosis. UVB-induced wrinkle formation, epidermal hyperplasia, and collagen degradation in mice skin was significantly inhibited when the photolyase was applied topically to the skin. These results demonstrated that rPHO has promising protective effects against UVB-induced photodamage and may contribute to the development of anti-UVB skin photodamage drugs and cosmetic products.
Keywords: DNA damage; oxidative stress; photorepair; recombinant photolyase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preparation of CPD Photolyase Nanoliposomes Derived from Antarctic Microalgae and Their Effect on UVB-Induced Skin Damage in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 2;23(23):15148. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315148. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499473 Free PMC article.
-
Photorepair of Either CPD or 6-4PP DNA Lesions in Basal Keratinocytes Attenuates Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Effects in Nucleotide Excision Repair Deficient Mice.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 29;13:800606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.800606. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35422806 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers from UVB exposure induce a hypermetabolic state in keratinocytes via mitochondrial oxidative stress.Redox Biol. 2021 Jan;38:101808. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101808. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 33264701 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity of rice to ultraviolet-B radiation.Ann Bot. 2006 Jun;97(6):933-42. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl044. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Ann Bot. 2006. PMID: 16520342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photolyases: capturing the light to battle skin cancer.Future Oncol. 2006 Apr;2(2):191-9. doi: 10.2217/14796694.2.2.191. Future Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16563088 Review.
Cited by
-
The Reduction of Skin Photodamage by the Ectoine-Thermus thermophilus Cofermentation Products.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jul;24(7):e70298. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70298. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40552640 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Protective Efficacy of Topical Products for Actinic Keratosis Against Ultraviolet-Induced DNA and Protein Damage: An Experimental, Double-Blind Irradiation Study.Cureus. 2023 Aug 24;15(8):e44065. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44065. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37746407 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of autophagy during photoaging reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory damage caused by UV.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 12;16:1562845. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1562845. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40421222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy protects against UVB-induced skin photoaging: A DNA-repairing mechanism involving the BER signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jul;28(14):e18536. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18536. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39044341 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

