Phloroglucinol Attenuates DNA Damage and Apoptosis Induced by Oxidative Stress in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium ARPE-19 Cells by Blocking the Production of Mitochondrial ROS
- PMID: 36552561
- PMCID: PMC9774705
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122353
Phloroglucinol Attenuates DNA Damage and Apoptosis Induced by Oxidative Stress in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium ARPE-19 Cells by Blocking the Production of Mitochondrial ROS
Abstract
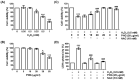
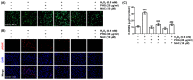
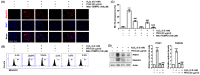
Phloroglucinol, a phenolic compound, is known to possess a potent antioxidant ability. However, its role in retinal cells susceptible to oxidative stress has not been well elucidated yet. Thus, the objective of this study was to evaluate whether phloroglucinol could protect against oxidative damage in cultured human retinal pigment epithelium ARPE-19 cells. For this purpose, ARPE-19 cells were stimula ted with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to mimic oxidative stress. Cell viability, cytotoxicity, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, mitochondrial function, DNA damage, and autophagy were then assessed. Our results revealed that phloroglucinol ameliorated cell viability, cytotoxicity, and DNA damage in H2O2-exposued ARPE-19 cells and blocked production of ROS. Phloroglucinol also counteracted H2O2-induced apoptosis by reducing Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, blocking activation of caspase-3, and inhibiting degradation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. H2O2 caused mitochondrial impairment and increased expression levels of mitophagy markers such as PINK1and PARKIN known to be associated with mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) generation and cytosolic release of cytochrome c. However, these changes were significantly attenuated by phloroglucinol. Mito-TEMPO, a selective mitochondrial antioxidant, further enhanced the protective effect of phloroglucinol against dysfunctional mitochondria. Furthermore, H2O2 induced autophagy, but not when ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with phloroglucinol, meaning that autophagy by H2O2 contributed to the pro-survival mechanism and that phloroglucinol protected ARPE-19 cells from apoptosis by blocking autophagy. Taken together, these results suggest that phloroglucinol can inhibit oxidative stress-induced ARPE-19 cell damage and dysfunction by protecting DNA damage, autophagy, and subsequent apoptosis through mitigation of mtROS generation. Thus, phloroglucinol might have therapeutic potential to prevent oxidative stress-mediated damage in RPE cells.
Keywords: DNA damage; apoptosis; autophagy; mitochondrial ROS; phloroglucinol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant signaling correlates with the preventive effect of loganin on oxidative injury in ARPE-19 human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Genes Genomics. 2023 Mar;45(3):271-284. doi: 10.1007/s13258-022-01302-4. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Genes Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36018494
-
Protective effect of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol against oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2019 Sep;38(3):298-308. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2019.1613425. Epub 2019 May 23. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31060395
-
Aloperine protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2022 Feb;42(1):88-94. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1850787. Epub 2020 Nov 30. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2022. PMID: 33256538
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in hearing loss: Oxidative stress, autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 20;11:1119773. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1119773. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36891515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corneal endothelial cells and acoustic cavitation in phacoemulsification.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Mar 16;11(8):1712-1718. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1712. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 36969995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lemon Peel Water Extract: A Novel Material for Retinal Health, Protecting Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells against Dynamin-Related Protein 1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission by Blocking ROS-Stimulated Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;13(5):538. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050538. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790643 Free PMC article.
-
Postbiotics in the Bakery Products: Applications and Nutritional Values.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Feb;17(1):292-314. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10327-y. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39066881 Review.
-
Exploring the anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic properties of phloroglucinol on pancreatic cells in diabetic models: In silico and in vivo study.Narra J. 2024 Dec;4(3):e1211. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i3.1211. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39816095 Free PMC article.
-
Phloroglucinol inhibited glycation via entrapping carbonyl intermediates.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 25;19(7):e0307708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307708. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39052603 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Disease Progression: A Blueprint for Mechanistic Understanding and Therapeutic Innovation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 31;14(1):38. doi: 10.3390/antiox14010038. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39857372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaarniranta K., Uusitalo H., Blasiak J., Felszeghy S., Kannan R., Kauppinen A., Salminen A., Sinha D., Ferrington D. Mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction and their impact on age-related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020;79:100858. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2021R1A2C200954911/Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government
- 2022R1I1A1A01070768/Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government
- 20220488/Korea Institute of Marine Science & Technology Promotion (KIMST) funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

