The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Plaque Stability
- PMID: 36552564
- PMCID: PMC9774534
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122356
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Plaque Stability
Abstract
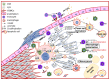
Atherosclerosis is the greatest contributor to cardiovascular events and is involved in the majority of deaths worldwide. Plaque rapture or erosion precipitates life-threatening thrombi, resulting in the obstruction blood flow to the heart (acute coronary syndrome), brain (ischemic stroke) or low extremities (peripheral vascular diseases). Among these events, major causation dues to the plaque rupture. Although the initiation, procession, and precise time of controlling plaque rupture are unclear, foam cell formation and apoptosis, cell death, extracellular matrix components, protease expression and activity, local inflammation, intraplaque hemorrhage, and calcification contribute to the plaque instability. These alterations tightly associate with the function regulation of intraplaque various cell populations. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is gasotransmitter derived from methionine metabolism and exerts a protective role in the genesis of atherosclerosis. Recent progress also showed H2S mediated the plaque stability. In this review, we discuss the progress of endogenous H2S modulation on functions of vascular smooth muscle cells, monocytes/macrophages, and T cells, and the molecular mechanism in plaque stability.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cystathionine gamma lyase; hydrogen sulfide; plaque stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular smooth muscle cell-derived hydrogen sulfide promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability via TFEB (transcription factor EB)-mediated autophagy.Autophagy. 2022 Oct;18(10):2270-2287. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2026097. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 35090378 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting hydrogen sulfide as a promising therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Mar 15;172(2):313-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.01.068. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24491853 Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jun;144:90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30959158
-
Sulfhydrated Sirtuin-1 Increasing Its Deacetylation Activity Is an Essential Epigenetics Mechanism of Anti-Atherogenesis by Hydrogen Sulfide.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Jan 10;30(2):184-197. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7195. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 29343087
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota in combination with blood metabolites reveals characteristics of the disease cluster of coronary artery disease and cognitive impairment: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 15;14:1308002. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308002. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38288114 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Epigenetic Regulation of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 8;24(16):12555. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612555. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628735 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Essential Functions of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Mar 4;15(3):198. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030198. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977089 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide and Oxygen Homeostasis in Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review from Molecular Biology to Therapeutic Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 6;24(9):8376. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098376. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu W., Cui C., Cui C., Chen Z., Zhang H., Cui Q., Xu G., Fan J., Han Y., Tang L., et al. Hepatocellular Cystathionine gamma lyase/Hydrogen sulfide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Activating Farnesoid X Receptor. Hepatology. 2022;76:1794–1810. doi: 10.1002/hep.32577. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franck G., Even G., Gautier A., Salinas M., Loste A., Procopio E., Gaston A.T., Morvan M., Dupont S., Deschildre C., et al. Haemodynamic stress-induced breaches of the arterial intima trigger inflammation and drive atherogenesis. Eur. Heart J. 2019;40:928–937. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy822. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

