Effects of a Phytogenic Supplement Containing Olive By-Product and Green Tea Extracts on Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism, and Hepatic Antioxidant Capacity in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Fed a High Soybean Meal Diet
- PMID: 36552623
- PMCID: PMC9774277
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122415
Effects of a Phytogenic Supplement Containing Olive By-Product and Green Tea Extracts on Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism, and Hepatic Antioxidant Capacity in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Fed a High Soybean Meal Diet
Abstract
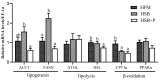
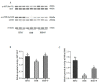
A 10-week growth trial was conducted to investigate the effects of a phytogenic feed additive (PFA) containing olive by-products and green tea extracts supplemented to a reduced fishmeal/high soybean meal diet on the growth performance, hepatic antioxidant capacity, lipid metabolism, and liver health of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Three experimental diets were tested: (1) a control high fishmeal (40%) and low soybean meal (15.57%) diet (named HFM), (2) a reduced fishmeal (30%) and high soybean meal (30.97%) diet (named HSB), and (3) a HSB diet supplemented with the PFA at 500 mg/kg (named HSB+P). Each diet was assigned to four replicate tanks, each containing 30 largemouth bass (initial body weight, IBW = 48.33 ± 0.01 g). The results showed that increasing the soybean meal content in the diet did not negatively affect growth performance, whereas supplementation with PFA significantly increased weight gain and specific growth rate of largemouth bass compared to both HFM and HSB groups. Reducing fishmeal and increasing soybean meal in the diet caused oxidative stress with a higher content of ROS in the liver. However, the hepatic antioxidant capacity was enhanced, with reduced ROS and increased GSH-Px levels in the HSB+P group. Moreover, the decrease of plasma TG, LDL-C, and LDL-C/TC, and downregulation of lipogenesis and cholesterol synthesis gene expression in liver, indicated that supplementation with the PFA improved fish lipid metabolism. Protein retention efficiency was also significantly increased in largemouth bass fed the diet with PFA supplementation, which regulated (enhanced) AKT-mTOR phosphorylation. These results clearly indicated that a PFA containing olive by-product and green tea extracts can positively improve growth performance, protein retention efficiency, antioxidant capacity, and lipid metabolism of largemouth bass fed a reduced fishmeal/high soybean meal diet.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; largemouth bass; lipid metabolism; phytogenic feed additive; soybean meal.
Conflict of interest statement
The author Morais, S., Pastor Jose J. and Gonçalves Rui A. are employed by Lucta S.A. and He M.L. is employed by Lucta (Guangzhou) Flavours Co., Ltd., respectively. They were involved in the funding acquisition, conceptualization, writing—review and editing, and decision to publish. The other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- FAO . FAO Yearbook Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics 2019. Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2021. p. 16.
-
- Zhu S.J., Gao W.H., Wen Z.Y., Chi S.Y., Shi Y.H., Hu W., Tan B.P. Partial substitution of fish meal by Clostridium autoethanogenum protein in the diets of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) Aquac. Rep. 2022;22:100938. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100938. - DOI
-
- Wang L., Wang J., Lu K.L., Song K., Mai K.S., Zhang C.X., Rahimnejad S. Total replacement of fish meal with soybean meal in diets for bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus): Effects on growth performance and gut microbial composition. Aquaculture. 2020;524:735236. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735236. - DOI
-
- Walsh S., Davis R., Weldon A., Reis J., Stites W., Rhodes M., Ibarra-Castro L., Bruce T., Davis D.A. Effects of fishmeal replacement, attractants, and taurine removal on juvenile and sub-adult Red Snapper (Lutjanus campechanus) Aquaculture. 2021;544:737054. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737054. - DOI
-
- Murashita K., Matsunari H., Furuita H., Rønnestad I., Oku H., Yamamoto T. Effects of dietary soybean meal on the digestive physiology of red seabream Pagrus major. Aquaculture. 2018;493:219–228. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.05.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

