Dioscin Protects against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Reducing Ferroptosis and Apoptosis through Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling
- PMID: 36552651
- PMCID: PMC9774127
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122443
Dioscin Protects against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Reducing Ferroptosis and Apoptosis through Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling
Abstract
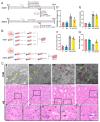
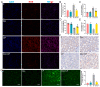
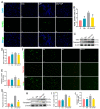
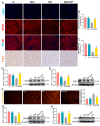
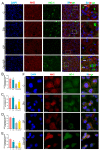
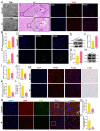
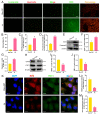
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a clinical syndrome with high morbidity and mortality worldwide, and there is currently no effective means to prevent it. Dioscin is naturally present in the dioscoreaceae plants and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Here, we found that dioscin is protective against cisplatin-induced AKI. Pathological and ultrastructural observations revealed that dioscin reduced renal tissue lesions and mitochondrial damage. Furthermore, dioscin markedly suppressed reactive oxygen species and malondialdehyde levels in the kidneys of AKI rats and increased the contents of glutathione and catalase. In addition, dioscin dramatically reduced the number of apoptotic cells and the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins in rat kidneys and human renal tubular epithelial cells (HK2). Conversely, the protein levels of anti-ferroptosis including GPX4 and FSP1 in vivo and in vitro were significantly enhanced after dioscin treatment. Mechanistically, dioscin promotes the entry of Nrf2 into the nucleus and regulates the expression of downstream HO-1 to exert renal protection. However, the nephroprotective effect of dioscin was weakened after inhibiting Nrf2 in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion, dioscin exerts a reno-protective effect by decreasing renal oxidative injury, apoptosis and ferroptosis through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, providing a new insight into AKI prevention.
Keywords: Nrf2/HO-1 signaling; acute kidney injury; apoptosis; dioscin; ferroptosis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dioscin exerts nephroprotective effects by attenuating oxidative stress and necroptosis-induced inflammation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Oct 25;140:112885. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112885. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39116496
-
Hazel Leaf Polyphenol Extract Alleviated Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Reducing Ferroptosis through Inhibiting Hippo Signaling.Molecules. 2024 Apr 11;29(8):1729. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081729. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675549 Free PMC article.
-
Paricalcitol Ameliorates Acute Kidney Injury in Mice by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):969. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020969. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674485 Free PMC article.
-
Role of curcumin in the treatment of acute kidney injury: research challenges and opportunities.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154306. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154306. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35809376 Review.
-
Plant Flavonoids on Oxidative Stress-Mediated Kidney Inflammation.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 26;11(12):1717. doi: 10.3390/biology11121717. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting ferroptosis: a new therapeutic opportunity for kidney diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 3;15:1435139. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1435139. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39021564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity: characteristics, common molecular mechanisms, and current clinical management.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024 Aug;28(8):711-727. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02490-x. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38678166 Review.
-
Cellular ROS and Antioxidants: Physiological and Pathological Role.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 14;13(5):602. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050602. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790707 Free PMC article.
-
Based on network pharmacology, the mechanism of Dioscin in alleviating renal tubular epithelial cell injury induced by calcium oxalate crystals was explored.Urolithiasis. 2024 Dec 12;53(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01673-1. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 39666011
-
Sesamin protects against Acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity by suppressing HMOX1-mediated apoptosis and ferroptosis.Redox Rep. 2025 Dec;30(1):2529695. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2025.2529695. Epub 2025 Jul 12. Redox Rep. 2025. PMID: 40650944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin F., Han S., Yu W., Rao T., Ruan Y., Yuan R., Li H., Ning J., Xia Y., Xie J., et al. microRNA-486-5p is implicated in the cisplatin-induced apoptosis and acute inflammation response of renal tubular epithelial cells by targeting HAT1. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022;36:e23039. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Jiang Y., Zhou W., Wu Y., Zhang S., Ding G., Zhang Y., Zhang A., Huang S., Jia Z., et al. Maintaining homeostasis of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum with NSC228155 alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022;181:270–287. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.02.003. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

