Correlation between Perturbation of Redox Homeostasis and Antibiofilm Capacity of Phytochemicals at Non-Lethal Concentrations
- PMID: 36552659
- PMCID: PMC9774353
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122451
Correlation between Perturbation of Redox Homeostasis and Antibiofilm Capacity of Phytochemicals at Non-Lethal Concentrations
Abstract
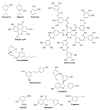
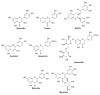
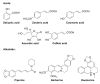
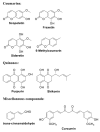
Biofilms are the multicellular lifestyle of microorganisms and are present on potentially every type of biotic or abiotic surface. Detrimental biofilms are generally targeted with antimicrobial compounds. Phytochemicals at sub-lethal concentrations seem to be an exciting alternative strategy to control biofilms, as they are less likely to impose selective pressure leading to resistance. This overview gathers the literature on individual phytocompounds rather than on extracts of which the use is difficult to reproduce. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first review to target only individual phytochemicals below inhibitory concentrations against biofilm formation. We explored whether there is an overall mechanism that can explain the effects of individual phytochemicals at sub-lethal concentrations. Interestingly, in all experiments reported here in which oxidative stress was investigated, a modest increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species was reported in treated cells compared to untreated specimens. At sub-lethal concentrations, polyphenolic substances likely act as pro-oxidants by disturbing the healthy redox cycle and causing an accumulation of reactive oxygen species.
Keywords: antioxidants and pro-oxidants; biocide-free antibiofilm substances; phenolic phytochemicals; reactive oxygen species; sub-lethal concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biofilm inhibition mechanism from extract of Hymenocallis littoralis leaves.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Aug 10;222:121-132. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.031. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29698774
-
The Untargeted Phytochemical Profile of Three Meliaceae Species Related to In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Anti-Virulence Activity against MRSA Isolates.Molecules. 2022 Jan 10;27(2):435. doi: 10.3390/molecules27020435. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35056761 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of plant extracts and phytochemicals against resistant Salmonella spp. in biofilms.Food Res Int. 2020 Feb;128:108806. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108806. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31955766 Review.
-
The Chemistry of Antibiofilm Phytocompounds.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(9):1034-1047. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666200807135243. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32767942 Review.
-
Antibiofilm activity of phytochemicals against Enterococcus faecalis: A literature review.Phytother Res. 2022 Jul;36(7):2824-2838. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7488. Epub 2022 May 6. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 35522168 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Efficiency of Pistacia lentiscus L. Derivates against Oral Biofilm-Associated Diseases-A Narrative Review.Microorganisms. 2023 May 24;11(6):1378. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061378. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37374880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Antibiofilm Potential of Natural Compounds by Targeting the NADH:quinone Oxidoreductase WrbA.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 14;12(8):1612. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081612. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelaalincy M.J., Navanietha Krishnaraj R., Shakambari G., Ashokkumar B., Kathiresan S., Varalakshmi P. Biofilm Engineering Approaches for Improving the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cells and Bioelectrochemical Systems. Front. Energy Res. 2018;6:63. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2018.00063. - DOI
-
- Sentenac H., Loyau A., Leflaive J., Schmeller D.S. The significance of biofilms to human, animal, plant and ecosystem health. Funct. Ecol. 2022;36:294–313. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13947. - DOI
-
- Mina I.R., Jara N.P., Criollo J.E., Castillo J.A. The critical role of biofilms in bacterial vascular plant pathogenesis. Plant Pathol. 2019;68:1439–1447. doi: 10.1111/ppa.13073. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

