Generation and Physiology of Hydrogen Sulfide and Reactive Sulfur Species in Bacteria
- PMID: 36552695
- PMCID: PMC9774590
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11122487
Generation and Physiology of Hydrogen Sulfide and Reactive Sulfur Species in Bacteria
Abstract
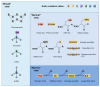
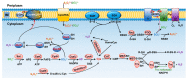
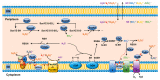
Sulfur is not only one of the most abundant elements on the Earth, but it is also essential to all living organisms. As life likely began and evolved in a hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-rich environment, sulfur metabolism represents an early form of energy generation via various reactions in prokaryotes and has driven the sulfur biogeochemical cycle since. It has long been known that H2S is toxic to cells at high concentrations, but now this gaseous molecule, at the physiological level, is recognized as a signaling molecule and a regulator of critical biological processes. Recently, many metabolites of H2S, collectively called reactive sulfur species (RSS), have been gradually appreciated as having similar or divergent regulatory roles compared with H2S in living organisms, especially mammals. In prokaryotes, even in bacteria, investigations into generation and physiology of RSS remain preliminary and an understanding of the relevant biological processes is still in its infancy. Despite this, recent and exciting advances in the fields are many. Here, we discuss abiotic and biotic generation of H2S/RSS, sulfur-transforming enzymes and their functioning mechanisms, and their physiological roles as well as the sensing and regulation of H2S/RSS.
Keywords: hydrogen sulfide; reactive sulfur species; sensing and regulation; sulfur transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sies H. Chapter 13—Oxidative Stress: Eustress and Distress in Redox Homeostasis. In: Fink G., editor. Stress: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pathology. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2019. pp. 153–163.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

