Male DAT Val559 Mice Exhibit Compulsive Behavior under Devalued Reward Conditions Accompanied by Cellular and Pharmacological Changes
- PMID: 36552823
- PMCID: PMC9777203
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11244059
Male DAT Val559 Mice Exhibit Compulsive Behavior under Devalued Reward Conditions Accompanied by Cellular and Pharmacological Changes
Abstract
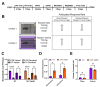
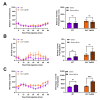
Identified across multiple psychiatric disorders, the dopamine (DA) transporter (DAT) Ala559Val substitution triggers non-vesicular, anomalous DA efflux (ADE), perturbing DA neurotransmission and behavior. We have shown that DAT Val559 mice display a waiting impulsivity and changes in cognitive performance associated with enhanced reward motivation. Here, utilizing a within-subject, lever-pressing paradigm designed to bias the formation of goal-directed or habitual behavior, we demonstrate that DAT Val559 mice modulate their nose poke behavior appropriately to match context, but demonstrate a perseverative checking behavior. Although DAT Val559 mice display no issues with the cognitive flexibility required to acquire and re-learn a visual pairwise discrimination task, devaluation of reward evoked habitual reward seeking in DAT Val559 mutants in operant tasks regardless of reinforcement schedule. The direct DA agonist apomorphine also elicits locomotor stereotypies in DAT Val559, but not WT mice. Our observation that dendritic spine density is increased in the dorsal medial striatum (DMS) of DAT Val559 mice speaks to an imbalance in striatal circuitry that might underlie the propensity of DAT Val559 mutants to exhibit compulsive behaviors when reward is devalued. Thus, DAT Val559 mice represent a model for dissection of how altered DA signaling perturbs circuits that normally balance habitual and goal-directed behaviors.
Keywords: animal model; compulsivity; dopamine transporter; goal; habit; impulsivity; instrumental learning; psychiatric disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

