Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Human Diseases Caused by Mutations of LINC Complex-Associated Genes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Summary
- PMID: 36552829
- PMCID: PMC9777268
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11244065
Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Human Diseases Caused by Mutations of LINC Complex-Associated Genes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Summary
Abstract
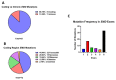
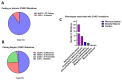
Mutations in genes encoding proteins associated with the linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex within the nuclear envelope cause different diseases with varying phenotypes including skeletal muscle, cardiac, metabolic, or nervous system pathologies. There is some understanding of the structure of LINC complex-associated proteins and how they interact, but it is unclear how mutations in genes encoding them can cause the same disease, and different diseases with different phenotypes. Here, published mutations in LINC complex-associated proteins were systematically reviewed and analyzed to ascertain whether patterns exist between the genetic sequence variants and clinical phenotypes. This revealed LMNA is the only LINC complex-associated gene in which mutations commonly cause distinct conditions, and there are no clear genotype-phenotype correlations. Clusters of LMNA variants causing striated muscle disease are located in exons 1 and 6, and metabolic disease-associated LMNA variants are frequently found in the tail of lamin A/C. Additionally, exon 6 of the emerin gene, EMD, may be a mutation "hot-spot", and diseases related to SYNE1, encoding nesprin-1, are most often caused by nonsense type mutations. These results provide insight into the diverse roles of LINC-complex proteins in human disease and provide direction for future gene-targeted therapy development.
Keywords: EMD; LINC complex; LMNA; SYNE1; emerin; lamin A/C; laminopathies; nesprin; nuclear envelope.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
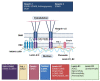
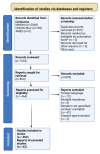
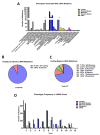
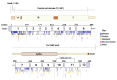
References
-
- Song S., Zhang Y., Zhong N. Laminopathies--One Gene, Multiple Diseases. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2005;37:96–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

