Astrocytic MicroRNAs and Transcription Factors in Alzheimer's Disease and Therapeutic Interventions
- PMID: 36552875
- PMCID: PMC9776935
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11244111
Astrocytic MicroRNAs and Transcription Factors in Alzheimer's Disease and Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
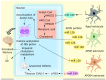
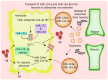
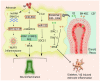
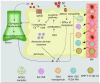
Astrocytes are important for maintaining cholesterol metabolism, glutamate uptake, and neurotransmission. Indeed, inflammatory processes and neurodegeneration contribute to the altered morphology, gene expression, and function of astrocytes. Astrocytes, in collaboration with numerous microRNAs, regulate brain cholesterol levels as well as glutamatergic and inflammatory signaling, all of which contribute to general brain homeostasis. Neural electrical activity, synaptic plasticity processes, learning, and memory are dependent on the astrocyte-neuron crosstalk. Here, we review the involvement of astrocytic microRNAs that potentially regulate cholesterol metabolism, glutamate uptake, and inflammation in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The interaction between astrocytic microRNAs and long non-coding RNA and transcription factors specific to astrocytes also contributes to the pathogenesis of AD. Thus, astrocytic microRNAs arise as a promising target, as AD conditions are a worldwide public health problem. This review examines novel therapeutic strategies to target astrocyte dysfunction in AD, such as lipid nanodiscs, engineered G protein-coupled receptors, extracellular vesicles, and nanoparticles.
Keywords: APOE4 nanodiscs; Astrocyte; Glutamate transporter 1; Transcriptional Factors; long non-coding RNA; microRNAs; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astrocytic transcription factors REST, YY1, and putative microRNAs in Parkinson's disease and advanced therapeutic strategies.Gene. 2024 Jan 20;892:147898. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147898. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Gene. 2024. PMID: 37832803 Review.
-
Astrocyte energy and neurotransmitter metabolism in Alzheimer's disease: Integration of the glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle.Prog Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;217:102331. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102331. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35872221 Review.
-
Deficient astrocyte metabolism impairs glutamine synthesis and neurotransmitter homeostasis in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Jan;148:105198. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105198. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 33242587
-
Calcineurin/NFAT Signaling in Activated Astrocytes Drives Network Hyperexcitability in Aβ-Bearing Mice.J Neurosci. 2017 Jun 21;37(25):6132-6148. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0877-17.2017. Epub 2017 May 30. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28559377 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: Neuroreparative properties and role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders.J Control Release. 2020 Jul 10;323:225-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.017. Epub 2020 Apr 11. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32289328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New perspectives on heterogeneity in astrocyte reactivity in neuroinflammation.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Jan 31;44:100948. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.100948. eCollection 2025 Mar. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40028234 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA 3222401L13Rik Is Upregulated in Aging Astrocytes and Regulates Neuronal Support Function Through Interaction with Npas3.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Jan 9;11(1):2. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11010002. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 39846680 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Alzheimer's Disease: Impact on Insulin Signaling and Advanced Drug Delivery Systems.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 28;13(3):157. doi: 10.3390/biology13030157. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the Role of Trem2 in Lipid Metabolism and Neuroinflammation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Apr;31(4):e70338. doi: 10.1111/cns.70338. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40205810 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Interactions with the Blood Brain Barrier: Insights from Drosophila and Implications for Human Astrocyte Targeted Therapies.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jan 20;50(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04333-x. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 39832031 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

