Using Second Measurement of De Ritis Ratio to Improve Mortality Prediction in Adult Trauma Patients in Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 36552937
- PMCID: PMC9776618
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12122930
Using Second Measurement of De Ritis Ratio to Improve Mortality Prediction in Adult Trauma Patients in Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
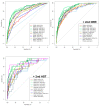
The De Ritis ratio (DRR), the ratio of serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase, has been reported to be a valuable biomarker in risk stratification for many liver and non-liver diseases. This study aimed to explore whether the inclusion of DRR at the date of intensive care unit (ICU) admission or days after ICU admission improves the predictive performance of various prognosis prediction models. This study reviewed 888 adult trauma patients (74 deaths and 814 survivors) in the trauma registered database between 1 January 2009, and 31 December 2020. Medical information with AST and ALT levels and derived DRR at the date of ICU admission (1st DRR) and 3-7 day after ICU admission (2nd DRR) was retrieved. Logistic regression was used to build new probability models for mortality prediction using additional DRR variables in various mortality prediction models. There was no significant difference in the 1st DRR between the death and survival patients; however, there was a significantly higher 2nd DRR in the death patients than the survival patients. This study showed that the inclusion of the additional DRR variable, measured 3-7 days after ICU admission, significantly increased the prediction performance in all studied prognosis prediction models.
Keywords: De Ritis ratio (DRR); alanine aminotransferase (ALT); aspartate aminotransferase (AST); intensive care unit (ICU); mortality; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of De Ritis ratio with aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase within the reference range.Clin Chim Acta. 2023 Jan 1;538:46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2022.11.005. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Clin Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 36370837
-
Delta De Ritis Ratio Is Associated with Worse Mortality Outcomes in Adult Trauma Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Traumatic Brain Injuries.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;12(12):3004. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123004. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553011 Free PMC article.
-
The reversed De Ritis ratio for predicting in-hospital mortality among intensive care patients with organophosphate poisoning.Biomarkers. 2023 Feb;28(1):111-117. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2022.2148746. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Biomarkers. 2023. PMID: 36377078
-
Elevated De Ritis Ratio Is Associated With Poor Prognosis in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 22;8:676581. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.676581. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 35004709 Free PMC article.
-
An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the De Ritis Ratio and Disease Severity and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19.Life (Basel). 2023 Jun 5;13(6):1324. doi: 10.3390/life13061324. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374107 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Prognostic Value of De Ritis Ratio on the Survival Rate of ICU-Admitted COVID-19 Patients During the Second Wave: A Retrospective Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India.Cureus. 2024 Jan 18;16(1):e52484. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52484. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38371091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mo Q., Liu Y., Zhou Z., Li R., Gong W., Xiang B., Tang W., Yu H. Prognostic Value of Aspartate Transaminase/Alanine Transaminase Ratio in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Hepatectomy. Front. Oncol. 2022;12:876900. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.876900. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Darstein F., Häuser F., Straub B.K., Wenzel J.J., Conradi R., Mittler J., Lang H., Galle P.R., Zimmermann T. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 is a common finding in liver-transplanted patients undergoing liver biopsy for elevated liver enzymes with a low De Ritis ratio and suspected acute rejection: A real-world cohort. Clin. Transpl. 2018;32:e13411. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13411. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

