Interplay between Myokine Profile and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Heart Failure
- PMID: 36552947
- PMCID: PMC9776539
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12122940
Interplay between Myokine Profile and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Heart Failure
Abstract
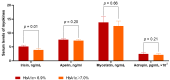
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) remains a powerful predictor of progressive heart failure (HF), but it is not clear whether altered glycemic control interferes with HF progression via an impaired profile of circulating myokines. The aim was to investigate plausible effects of glucose control on a myokine signature in T2DM patients affected by chronic HF. We selected 372 T2DM patients from the local database and finally included 314 individuals suffering from chronic HF and subdivided them into two groups according to glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (<6.9% and ≥7.0%). Echocardiography and Doppler examinations along with biomarker measurements were performed at the baseline of the study. The results showed that irisin levels were significantly lower in patients with HbA1c ≥ 7.0% than in those with HbAc1 < 6.9%, whereas concentrations of apelin, myostatin and adropin did not significantly differ between these two groups. We also identified numerous predictors of poor glycemic control, but only N-terminal brain natriuretic propeptide (odds ratio [OR] = 1.07; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.02−1.10, p = 0.04) and irisin (OR = 1.09; 95% CI = 1.04−1.17, p = 0.001) remained independent predictors of the dependent variable. In conclusion, we found that decreased levels of irisin were associated with poor glycemic control in T2DM patients with HF regardless of clinical conditions and other biomarkers.
Keywords: adropin; apelin; biomarkers; heart failure; irisin; myokines; myostatin; prediction; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of Kidney Function Outcomes and Their Relation to SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Who Had Chronic Heart Failure.Adv Ther. 2024 Jan;41(1):292-314. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02683-y. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 37935870 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Circulating MicroRNAs and Myokines and Interactions with Serum Osteopontin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Moderate and Poor Glycemic Control: A Biochemical and Molecular Study.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Dec 7;2021:7453000. doi: 10.1155/2021/7453000. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34917685 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Levels of Irisin Predict Cumulative Clinical Outcomes in Heart Failure Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Physiol. 2022 May 16;13:922775. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.922775. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35651870 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Myokines as Novel Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Diseases.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 5;25(2):56. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2502056. eCollection 2024 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39077334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adropin and irisin in arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Nov;28(11):1571-1575. doi: 10.17219/acem/104551. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 31756066 Review.
Cited by
-
Adropin Predicts Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Chronic Heart Failure.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 13;12(6):2231. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062231. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983232 Free PMC article.
-
Adropin Predicts Asymptomatic Heart Failure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Independent of the Levels of Natriuretic Peptides.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;14(16):1728. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161728. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202216 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Glucose Control with Circulating Levels of Red Blood Cell-Derived Vesicles in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Atrial Fibrillation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 31;24(1):729. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010729. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614172 Free PMC article.
-
Low Levels of Adropin Predict Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Outpatients with Newly Diagnosed Prediabetes after Acute Myocardial Infarction.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 15;12(8):1857. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081857. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200321 Free PMC article.
-
Low Plasma Levels of Irisin Predict Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Chronic Heart Failure.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Mar 23;10(4):136. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10040136. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37103015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Aparicio H.J., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2021 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e254–e743. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouthoorn S., Valstar G.B., Gohar A., Ruijter H.D., Reitsma H.B., Hoes A.W., Rutten F.H. The prevalence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in men and women with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018;15:477–493. doi: 10.1177/1479164118787415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gohar A., Kievit R.F., Valstar G.B., Hoes A.W., E Van Riet E., Van Mourik Y., Bertens L.C., Boonman-Winter L.J., Bots M.L., Ruijter H.D., et al. Opportunistic screening models for high-risk men and women to detect diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the community. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018;26:613–623. doi: 10.1177/2047487318816774. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

