Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid-Isolated Biomarkers for the Diagnostic and Prognostic Assessment of Lung Cancer
- PMID: 36552956
- PMCID: PMC9776496
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12122949
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid-Isolated Biomarkers for the Diagnostic and Prognostic Assessment of Lung Cancer
Abstract
Lung cancer is considered one of the most fatal malignant neoplasms because of its late detection. Detecting molecular markers in samples from routine bronchoscopy, including many liquid-based cytology procedures, such as bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), could serve as a favorable technique to enhance the efficiency of a lung cancer diagnosis. BALF analysis is a promising approach to evaluating the tumor progression microenvironment. BALF's cellular and non-cellular components dictate the inflammatory response in a cancer-proliferating microenvironment. Furthermore, it is an essential material for detecting clinically significant predictive and prognostic biomarkers that may aid in guiding treatment choices and evaluating therapy-induced toxicities in lung cancer. In the present article, we have reviewed recent literature about the utility of BALF analysis for detecting markers in different stages of tumor cell metabolism, employing either specific biomarker assays or broader omics approaches.
Keywords: biomarkers; bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; lung neoplasm; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
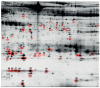
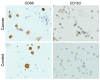
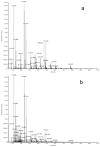
References
-
- Howlader N., Noone A., Krapcho M., Miller D., Brest A., Yu M., Ruhl J., Tatalovich Z., Mariotto A., Lewis D., et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2021.
-
- Wongsurakiat P., Wongbunnate S., Dejsomritrutai W., Charoenratanakul S., Tscheikuna J., Youngchaiyud P., Pushpakom R., Maranetra N., Nana A., Chierakul N., et al. Diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage and postbronchoscopic sputum cytology in peripheral lung cancer. Respirology. 1998;3:131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.1998.tb00111.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

