Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension
- PMID: 36552997
- PMCID: PMC9776885
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12122990
Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension
Abstract
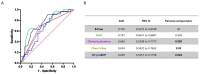
Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is a frequent and well-known complication of hemodialysis, occurring in about one third of patients. An integrated approach with different methods is needed to minimize IDH episodes and their complications. In this prospective observational study, recruited patients underwent a multiparametric evaluation of fluid status through a lung ultrasound (LUS) with the quantification of B-lines, a physical examination, blood pressure, NT-proBNP and chest X-rays. The evaluation took place immediately before and at the end of the dialysis session, and the patients were divided into IDH and no-IDH groups. We recruited a total of 107 patients. A pre-dialysis B-line number ≥ 15 showed a high sensitivity in fluid overload diagnosis (94.5%), even higher than a chest X-ray (78%) or physical examination (72%) alone. The identification at the beginning of dialysis of <8 B-lines in the overall cohort or <20 B-lines in patients with NYHA 3−4 class are optimal thresholds for identifying those patients at higher risk of experiencing an IDH episode. In the multivariable analysis, the NYHA class, a low pre-dialysis systolic BP and a low pre-dialysis B-line number were independent risk factors for IDH. At the beginning of dialysis, the B-line quantification at LUS is a valuable and reliable method for evaluating fluid status and predicting IDH episodes. A post-dialysis B-line number <5 may allow for an understanding of whether the IDH episode was caused by dehydration, probably due to due to an overestimation of the dry weight.
Keywords: B-lines; dry weight; fluid overload; intradialytic hypotension; lung ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- K/DOQI Workgroup K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2005;45:S1–S153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

