MRI-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Predicting Prostate Cancer with Gray-Zone Prostate-Specific Antigen Levels to Reduce Unnecessary Biopsies
- PMID: 36553012
- PMCID: PMC9776817
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12123005
MRI-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Predicting Prostate Cancer with Gray-Zone Prostate-Specific Antigen Levels to Reduce Unnecessary Biopsies
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to establish a predictive nomogram for predicting prostate cancer (PCa) in patients with gray-zone prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels (4-10.0 ng/mL) based on radiomics and other traditional clinical parameters.
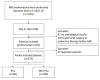
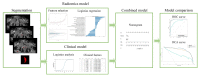
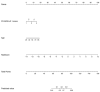
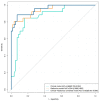
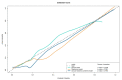
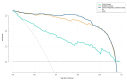
Methods: In all, 274 patients with gray-zone PSA levels were included in this retrospective study. They were randomly divided into training and validation sets (n = 191 and 83, respectively). Data on the clinical risk factors related to PCa with gray-zone PSA levels (such as Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System, version 2.1 [PI-RADS V2.1] category, age, prostate volume, and serum PSA level) were collected for all patients. Lesion volumes of interest (VOI) from T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) imaging were annotated by two radiologists. The radiomics model, clinical model, and combined prediction model, which was presented on a nomogram by incorporating the radiomics signature and clinical and radiological risk factors for PCa, were developed using logistic regression. The area under the receiver operator characteristic (AUC-ROC) and decision, calibration curve were used to compare the three models for the diagnosis of PCa with gray-zone PSA levels.
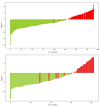
Results: The predictive nomogram (AUC: 0.953) incorporating the radiomics score and PI-RADS V2.1 category, age, and the radiomics model (AUC: 0.941) afforded much higher diagnostic efficacy than the clinical model (AUC: 0.866). The addition of the rad score could improve the discriminatory performance of the clinical model. The decision curve analysis indicated that the radiomics or combined model could be more beneficial compared to the clinical model for the prediction of PCa. The nomogram showed good agreement for detecting PCa with gray-zone PSA levels between prediction and histopathologic confirmation.
Conclusion: The nomogram, which combined the radiomics score and PI-RADS V2.1 category and age, is an effective and non-invasive method for predicting PCa. Furthermore, as well as good calibration and is clinically useful, which could reduce unnecessary prostate biopsies in patients having PCa with gray-zone PSA levels.
Keywords: MRI; biopsies; prostate cancer; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roobol M.J., Kranse R., Bangma C.H., van Leenders A.G., Blijenberg B.G., van Schaik R.H., Kirkels W.J., Otto S.J., van der Kwast T.H., de Koning H.J., et al. Screening for prostate cancer: Results of the Rotterdam section of the European randomized study of screening for prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013;64:530–539. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.05.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen R., Huang Y.R., Cai X.B., Xie L.P., He D.L., Zhou L.Q., Xu C.L., Gao X., Ren S.C., Wang F.B., et al. Age-Specific Cutoff Value for the Application of Percent Free Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) in Chinese Men with Serum PSA Levels of 4.0–10.0 ng/mL. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0130308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

