Cleft Lip and/or Cleft Palate: Prenatal Accuracy, Postnatal Course, and Long-Term Outcomes
- PMID: 36553322
- PMCID: PMC9776564
- DOI: 10.3390/children9121880
Cleft Lip and/or Cleft Palate: Prenatal Accuracy, Postnatal Course, and Long-Term Outcomes
Abstract
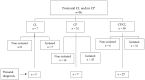
Orofacial clefts include cleft lip (CL) and cleft palate (CP). This retrospective study assessed the efficacy of prenatal sonographic diagnosis of isolated and non-isolated cases of CL/CP and the postnatal outcomes of these children. Data regarding patients diagnosed and treated in the tertiary orofacial clinic from 2000 to 2020 were retrieved from electronic medical records and telephone-based questionnaires. Isolated CL was found in 7 cases (7.2%), isolated CP in 51 (53%), and combined CL/CP in 38 (39.5%), and 22 cases (23%) were associated with other anomalies. Among 96 cases, 39 (40.6%) were diagnosed prenatally. Isolated CL was diagnosed in 5/7 (71.5%), combined clefts in 29/38 (76.3%), and CP in 7/51 (13.8%). Prenatal chromosomal analysis performed in 32/39 (82%) cases was normal for all. The rate of surgical intervention in the first year of life was 36/38 (94.7%) for combined clefts, 5/7 (71.4%) for CL, and 20/51 (39%) for isolated CP. Most children had speech therapy (23/38 (60.5%), 3/7 (42.8%), and 41/51 (80.3%), respectively) and psychotherapy (6/38 (15.7%), 3/7 (42.8%) and, 15/51 (29.4%), respectively). The accuracy rate of sonographic prenatal diagnosis is low. Our results emphasize the suggested work-up of fetuses with CL and/or CP and improvements to parental counseling, as well as their understanding and compliance regarding post-natal therapeutic plans.
Keywords: anomaly scan; cleft lip; cleft palate; post-natal; prenatal diagnosis; ultrasound diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Chmait R., Pretorius D., Moore T., Hull A., James G., Nelson T., Jones M. Prenatal detection of associated anomalies in fetuses diagnosed with cleft lip with or without cleft palate in utero. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2006;27:173–176. doi: 10.1002/uog.2593. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous