Accuracy of Algorithms Predicting Accessory Pathway Localization in Pediatric Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
- PMID: 36553406
- PMCID: PMC9776491
- DOI: 10.3390/children9121962
Accuracy of Algorithms Predicting Accessory Pathway Localization in Pediatric Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
Abstract
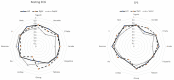
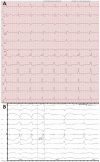
We aimed to assess the accuracy of determining accessory pathway (AP) localization from 12 lead ECG tracings by applying 12 different algorithms in pediatric patients diagnosed with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. We compared algorithm accuracy in electrophysiologic study ECG tracings with full preexcitation and resting ECG tracings. The assessing pediatric cardiologists were blinded regarding EP study results on AP localization. For exact AP location, the algorithms published by D'Avila et al. and Boersma et al. yielded the highest accuracy (58%). Distinguishing laterality, the median accuracy for predicting left or right-sided APs was 74%, while for septal APs it was 68%. We conclude that algorithms predicting AP location in pediatric patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome show low accuracy for exact AP localization. For laterality, however, accuracy was significantly higher.
Keywords: ECG; WPW syndrome; ablation; electrophysiology; pathway localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased preexcitation on electrocardiography improves accuracy of algorithms for accessory pathway localization in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.Kardiol Pol. 2020 Jun 25;78(6):567-573. doi: 10.33963/KP.15378. Epub 2020 May 20. Kardiol Pol. 2020. PMID: 32438794
-
Comparison of the accuracy of three algorithms in predicting accessory pathways among adult Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome patients.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015 Dec;44(3):213-9. doi: 10.1007/s10840-015-0057-6. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26384677
-
A Novel and Simple Algorithm Using Surface Electrocardiogram That Localizes Accessory Conduction Pathway in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in Pediatric Patients.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019 Sep;35(5):493-500. doi: 10.6515/ACS.201909_35(5).20190312A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019. PMID: 31571798 Free PMC article.
-
Algorithms to Identify Accessory Pathways' Location on the 12-Lead Electrocardiogram.Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2020 Dec;12(4):465-474. doi: 10.1016/j.ccep.2020.08.007. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2020. PMID: 33161996 Review.
-
The use of echocardiography in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012 Apr;28(4):725-34. doi: 10.1007/s10554-011-9880-8. Epub 2011 May 1. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012. PMID: 21533788 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Focal cryoablation vs. radiofrequency ablation in a pediatric patient with para-Hisian accessory pathway with effect from the non-coronary aortic cusp.Front Pediatr. 2024 Aug 20;12:1405104. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1405104. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39228439 Free PMC article.
-
A computational study on the influence of antegrade accessory pathway location on the 12-lead electrocardiogram in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.Europace. 2025 Feb 5;27(2):euae223. doi: 10.1093/europace/euae223. Europace. 2025. PMID: 39259657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brugada J., Blom N., Sarquella-Brugada G., Blomstrom-Lundqvist C., Deanfield J., Janousek J., Abrams D., Bauersfeld U., Brugada R., Drago F., et al. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapy for arrhythmias in the pediatric population: EHRA and AEPC-Arrhythmia Working Group joint consensus statement. Europace. 2013;15:1337–1382. doi: 10.1093/europace/eut082. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kugler J.D., Danford D.A., Houston K.A., Felix G. Pediatric radiofrequency catheter ablation registry success, fluoroscopy time, and complication rate for supraventricular tachycardia: Comparison of early and recent eras. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2002;13:336–341. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2002.00336.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arruda M.S., McClelland J.H., Wang X., Beckman K.J., Widman L.E., Gonzalez M.D., Nakagawa H., Lazzara R., Jackman W.M. Development and validation of an ECG algorithm for identifying accessory pathway ablation site in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1998;9:2–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1998.tb00861.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chiang C.E., Chen S.A., Teo W.S., Tsai D.S., Wu T.J., Cheng C.C., Chiou C.W., Tai C.T., Lee S.H., Chen C.Y., et al. An accurate stepwise electrocardiographic algorithm for localization of accessory pathways in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome from a comprehensive analysis of delta waves and R/S ratio during sinus rhythm. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995;76:40–46. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(99)80798-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

