Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 36553449
- PMCID: PMC9778480
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122183
Mechanisms of EGFR-TKI-Induced Apoptosis and Strategies Targeting Apoptosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
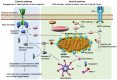
Homeostasis is achieved by balancing cell survival and death. In cancer cells, especially those carrying driver mutations, the processes and signals that promote apoptosis are inhibited, facilitating the survival and proliferation of these dysregulated cells. Apoptosis induction is an important mechanism underlying the therapeutic efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the mechanisms by which EGFR-TKIs induce apoptosis have not been fully elucidated. A deeper understanding of the apoptotic pathways induced by EGFR-TKIs is essential for the developing novel strategies to overcome resistance to EGFR-TKIs or to enhance the initial efficacy through therapeutic synergistic combinations. Recently, therapeutic strategies targeting apoptosis have been developed for cancer. Here, we review the state of knowledge on EGFR-TKI-induced apoptotic pathways and discuss the therapeutic strategies for enhancing EGFR-TKI efficiency. We highlight the great progress achieved with third-generation EGFR-TKIs. In particular, combination therapies of EGFR-TKIs with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor/receptor inhibitors or chemotherapy have emerged as promising therapeutic strategies for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Nevertheless, further breakthroughs are needed to yield an appropriate standard care for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC, which requires gaining a deeper understanding of cancer cell dynamics in response to EGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; EGFR-mutated NSCLC; apoptosis; combination therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
T.Y. receives commercial research support from Boehringer Ingelheim. J.T. receives research funding and lecture fees from Eisai, Taiho, Eli Lilly, Kyowa Kirin, Astra Zeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Fundacion San Juan de Dios, and West Japan Oncology Group. J.T. is an advisor to Astra Zeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Seagen, and Eli Lilly. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Janmaat M.L., Kruyt F.A., Rodriguez J.A., Giaccone G. Response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells: Limited antiproliferative effects and absence of apoptosis associated with persistent activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase or Akt kinase pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003;9:2316–2326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous