White Sponge Nevus Caused by Keratin 4 Gene Mutation: A Case Report
- PMID: 36553451
- PMCID: PMC9777919
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122184
White Sponge Nevus Caused by Keratin 4 Gene Mutation: A Case Report
Abstract
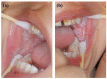
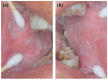
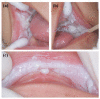
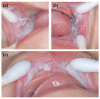
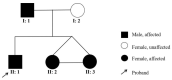
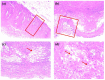
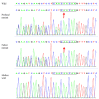
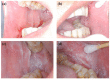
White sponge nevus (WSN) is a rare autosomal dominant disease with a family history, often caused by mutations of the keratin 4 (K4) and keratin 13 (K13) genes in patients. It is characterized by frequently occurred white corrugated folds in the bilateral buccal mucosa with soft texture. On histopathological examination, hyperkeratosis of epithelial cells, edema, and vacuolar changes in the spinous cells are observed in the lesions, despite a normal layer of basal cells. WSN should be differentiated from other oral white spot diseases, mainly oral lichen planus, oral candidiasis, oral white edema, and Heck's disease, to reduce misdiagnosis and unnecessary treatment. At present, there is no specific treatment method. The purpose of this study was to report the clinical data of four WSN patients of the same family with the K4 gene mutation. The occurrence of WSN in a pair of monozygotic twins with very similar clinical presentations was identified for the first time. The gene sequencing results showed that there was a heterozygous deletion (C. 438_440delCAA) in exon 1 of the K4 gene, resulting in an aspartic acid loss in both the proband and his father. Finally, the etiology, pathogenesis, pathological manifestations, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and related treatment methods are discussed to provide a reference for clinical treatment of the disease.
Keywords: K4; WSN; gene mutation; genetic disorder; recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Q.M. Oral Mucosal Pathology. 5th ed. People’s Medical Publishing House; Beijing, China: 2020. pp. 107–108.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

