Co-Occurrence of a Pathogenic HSD3B2 Variant and a Duplication on 10q22.3-q23.2 Detected in Newborn Twins with Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- PMID: 36553457
- PMCID: PMC9777535
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122190
Co-Occurrence of a Pathogenic HSD3B2 Variant and a Duplication on 10q22.3-q23.2 Detected in Newborn Twins with Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Abstract
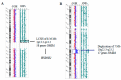
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies required for cortisol biosynthesis in the adrenal cortex. The majority of CAH are due to the deficiency of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme, while 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 deficiency accounts for less than five percent of all CAH cases. We report two Moroccan twins from a spontaneous triplet pregnancy. The 46,XY newborn exhibited a disorder of sexual differentiation (DSD) with hypo virilization, while the 46,XX newborn had normal female external genitalia. In the first week of life, they showed hyponatremia and primary adrenal insufficiency with a slight 17OHP elevation and increased DHEAS and renin levels. The aCGH-SNP analysis disclosed a 8.36 Mb long contiguous stretch of homozygosity (LCSH) on chromosome 1p13.2-p11.2 including the candidate HSD3B2 gene, a LCSH of 7.3 Mb on 14q31.1-q32.11, and a 7 Mb duplication on 10q22.3-q23.2. Clinical exome sequencing revealed the biallelic c.969T > G (p.Asn323Lys) HSD3B2, likely pathogenic, variant in both of the affected twins. This case emphasizes the importance of a prompt molecular diagnosis performed through the combination of aCGH and clinical exome, both for establishment of correct therapy and for follow-up, as the newborns also carry a genomic rearrangement with possible clinical implications.
Keywords: HSD3B2; LCSH; aCGH-SNP; congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel homozygous Q334X mutation in the HSD3B2 gene causing classic 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency: an unexpected diagnosis after a positive newborn screen for 21-hydroxylase deficiency.Horm Res Paediatr. 2012;77(5):334-8. doi: 10.1159/000336004. Epub 2012 Feb 9. Horm Res Paediatr. 2012. PMID: 22343390
-
Structural aspects of the p.P222Q homozygous mutation of HSD3B2 gene in a patient with congenital adrenal hyperplasia.Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2010 Nov;54(8):768-74. doi: 10.1590/s0004-27302010000800018. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2010. PMID: 21340167
-
3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II deficiency on newborn screening test.Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2014 Aug;58(6):650-5. doi: 10.1590/0004-2730000003098. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2014. PMID: 25211449
-
[Congenital adrenal hyperplasia].Med Pregl. 1999 Nov-Dec;52(11-12):447-54. Med Pregl. 1999. PMID: 10748766 Review. Croatian.
-
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: update on prenatal diagnosis and treatment.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999 Apr-Jun;69(1-6):19-29. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(99)00059-x. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10418977 Review.
Cited by
-
Addison's Disease: Diagnosis and Management Strategies.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Jun 2;16:2187-2210. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S390793. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37287503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

