Bioinformatics Prediction and Machine Learning on Gene Expression Data Identifies Novel Gene Candidates in Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 36553500
- PMCID: PMC9778573
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122233
Bioinformatics Prediction and Machine Learning on Gene Expression Data Identifies Novel Gene Candidates in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the five most common cancers in the world and unfortunately has a high mortality rate. To date, the pathogenesis and disease genes of GC are unclear, so the need for new diagnostic and prognostic strategies for GC is undeniable. Despite particular findings in this regard, a holistic approach encompassing molecular data from different biological levels for GC has been lacking. To translate Big Data into system-level biomarkers, in this study, we integrated three different GC gene expression data with three different biological networks for the first time and captured biologically significant (i.e., reporter) transcripts, hub proteins, transcription factors, and receptor molecules of GC. We analyzed the revealed biomolecules with independent RNA-seq data for their diagnostic and prognostic capabilities. While this holistic approach uncovered biomolecules already associated with GC, it also revealed novel system biomarker candidates for GC. Classification performances of novel candidate biomarkers with machine learning approaches were investigated. With this study, AES, CEBPZ, GRK6, HPGDS, SKIL, and SP3 were identified for the first time as diagnostic and/or prognostic biomarker candidates for GC. Consequently, we have provided valuable data for further experimental and clinical efforts that may be useful for the diagnosis and/or prognosis of GC.
Keywords: diagnostic genes; disease genes; gastric cancer; multi-omics; prognostic genes; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
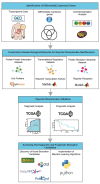
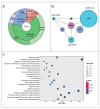
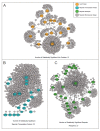

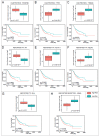
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

