EpiReSIM: A Resampling Method of Epistatic Model without Marginal Effects Using Under-Determined System of Equations
- PMID: 36553553
- PMCID: PMC9777644
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122286
EpiReSIM: A Resampling Method of Epistatic Model without Marginal Effects Using Under-Determined System of Equations
Abstract
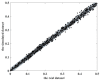
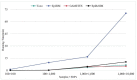
Simulation experiments are essential to evaluate epistasis detection methods, which is the main way to prove their effectiveness and move toward practical applications. However, due to the lack of effective simulators, especially for simulating models without marginal effects (eNME models), epistasis detection methods can hardly verify their effectiveness through simulation experiments. In this study, we propose a resampling simulation method (EpiReSIM) for generating the eNME model. First, EpiReSIM provides two strategies for solving eNME models. One is to calculate eNME models using prevalence constraints, and another is by joint constraints of prevalence and heritability. We transform the computation of the model into the problem of solving the under-determined system of equations. Introducing the complete orthogonal decomposition method and Newton's method, EpiReSIM calculates the solution of the underdetermined system of equations to obtain the eNME model, especially the solution of the high-order model, which is the highlight of EpiReSIM. Second, based on the computed eNME model, EpiReSIM generates simulation data by a resampling method. Experimental results show that EpiReSIM has advantages in preserving the biological properties of minor allele frequencies and calculating high-order models, and it is a convenient and effective alternative method for current simulation software.
Keywords: GWAS; epistasis model; heritability; penetrance table; prevalence; resampling; simulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shang J., Zhang J., Lei X., Zhao W., Dong Y. EpiSIM: Simulation of multiple epistasis, linkage disequilibrium patterns and haplotype blocks for genome-wide interaction analysis. Genes Genom. 2013;35:305–316. doi: 10.1007/s13258-013-0081-9. - DOI
-
- Sun Y., Shang J., Liu J., Li S. An Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for the Detection of SNP-SNP Interactions; Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing; Lanzhou, China. 2–5 August 2016; pp. 21–32. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources