Complete Plastome of Physalis angulata var. villosa, Gene Organization, Comparative Genomics and Phylogenetic Relationships among Solanaceae
- PMID: 36553558
- PMCID: PMC9778145
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122291
Complete Plastome of Physalis angulata var. villosa, Gene Organization, Comparative Genomics and Phylogenetic Relationships among Solanaceae
Abstract
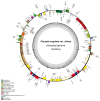
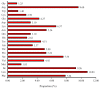
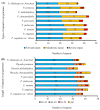
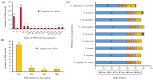
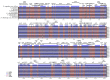
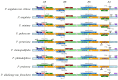
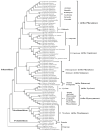
Physalis angulata var. villosa, rich in withanolides, has been used as a traditional Chinese medicine for many years. To date, few extensive molecular studies of this plant have been conducted. In the present study, the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa was sequenced, characterized and compared with that of other Physalis species, and a phylogenetic analysis was conducted in the family Solanaceae. The plastome of P. angulata var. villosa was 156,898 bp in length with a GC content of 37.52%, and exhibited a quadripartite structure typical of land plants, consisting of a large single-copy (LSC, 87,108 bp) region, a small single-copy (SSC, 18,462 bp) region and a pair of inverted repeats (IR: IRA and IRB, 25,664 bp each). The plastome contained 131 genes, of which 114 were unique and 17 were duplicated in IR regions. The genome consisted of 85 protein-coding genes, eight rRNA genes and 38 tRNA genes. A total of 38 long, repeat sequences of three types were identified in the plastome, of which forward repeats had the highest frequency. Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) analysis revealed a total of 57 SSRs, of which the T mononucleotide constituted the majority, with most of SSRs being located in the intergenic spacer regions. Comparative genomic analysis among nine Physalis species revealed that the single-copy regions were less conserved than the pair of inverted repeats, with most of the variation being found in the intergenic spacer regions rather than in the coding regions. Phylogenetic analysis indicated a close relationship between Physalis and Withania. In addition, Iochroma, Dunalia, Saracha and Eriolarynx were paraphyletic, and clustered together in the phylogenetic tree. Our study published the first sequence and assembly of the plastome of P. angulata var. villosa, reported its basic resources for evolutionary studies and provided an important tool for evaluating the phylogenetic relationship within the family Solanaceae.
Keywords: Physalis angulata var. villosa; SSRs; comparative genomics; phylogenetic relationship; plastome; repeat analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Barleria prionitis, comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetic relationships among Acanthoideae.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jun 6;21(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06798-2. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32532210 Free PMC article.
-
Complete chloroplast genomes of four Physalis species (Solanaceae): lights into genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 May 28;20(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02429-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32466748 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the plastome of Physaliscordata and comparative analysis of eight species of Physalis sensu stricto.PhytoKeys. 2022 Oct 5;210:109-134. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.210.85668. eCollection 2022. PhytoKeys. 2022. PMID: 36760406 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of plastome evolution in autotrophic Piperales.Am J Bot. 2024 Mar;111(3):e16300. doi: 10.1002/ajb2.16300. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Am J Bot. 2024. PMID: 38469876 Review.
-
Physalis angulata Linn. as a medicinal plant (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Jan 24;20(3):47. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1735. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38357237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Untargeted Chemical Profile, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibition Activity of Physalis angulata L. from the Peruvian Amazon: A Contribution to the Validation of Its Pharmacological Potential.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;14(3):246. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030246. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227212 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Chloroplast Microsatellite Markers and Evaluation of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Cutleaf Groundcherry (Physalis angulata L.) in China.Plants (Basel). 2023 Apr 25;12(9):1755. doi: 10.3390/plants12091755. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37176816 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Physalis molecular research: applications in authentication, genetic diversity, phylogenetics, functional genes, and omics.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 27;15:1407625. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1407625. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38993935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plastomes of Garcinia mangostana L. and Comparative Analysis with Other Garcinia Species.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;12(4):930. doi: 10.3390/plants12040930. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese academy of sciences . Flora of China. Volume 67. Science Press; Beijing, China: 1978. p. 58.
-
- Ma T., Zhang W.N., Yang L., Zhang C., Lin R., Shan S.M., Zhu M.D., Luo J.G., Kong L.Y. Cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulata var. villosa and the apoptosis-inducing effect via ROS generation and the activation of MAPK in human osteosarcoma cells. Rsc. Adv. 2016;6:53089–53100. doi: 10.1039/C6RA08574A. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

