Bta-miR-106b Regulates Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell Proliferation, Cell Cycle, and Milk Protein Synthesis by Targeting the CDKN1A Gene
- PMID: 36553575
- PMCID: PMC9777812
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122308
Bta-miR-106b Regulates Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell Proliferation, Cell Cycle, and Milk Protein Synthesis by Targeting the CDKN1A Gene
Abstract
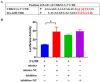
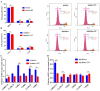
Our previous studies found that bta-miR-106b and its corresponding target gene, CDKN1A, were differentially expressed between the mammary epithelium of lactating Holstein cows with extremely high and low milk protein and fat percentage, implying the potential role of bta-miR-106b in milk composition synthesis. In this study, with luciferase assay experiment, bta-miR-106b was validated to target the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of bovine CDKN1A, thereby regulating its expression. Moreover, in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs), over-expression of bta-miR-106b significantly down-regulated the CDKN1A expression at both mRNA and protein levels, and inhibitors of bta-miR-106b increased CDKN1A expression. Of note, we observed that bta-miR-106b accelerated cell proliferation and cell cycle, and changed the expressions of protein synthesis related pathways such as JAK-STAT and PI3K/AKT/mTOR through regulating CDKN1A expression. Our findings highlight the important regulatory role of bta-miR-106b in milk protein synthesis by targeting CDKN1A in dairy cattle.
Keywords: BMECs; CDKN1A; bta-miR-106b; cell proliferation; milk protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

