Ploidy Status, Nuclear DNA Content and Start Codon Targeted (SCoT) Genetic Homogeneity Assessment in Digitalis purpurea L., Regenerated In Vitro
- PMID: 36553602
- PMCID: PMC9777722
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122335
Ploidy Status, Nuclear DNA Content and Start Codon Targeted (SCoT) Genetic Homogeneity Assessment in Digitalis purpurea L., Regenerated In Vitro
Abstract
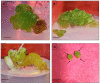
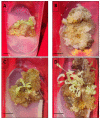
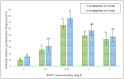
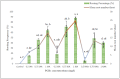
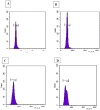
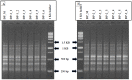
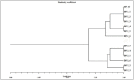
Digitalis purpurea L. is a therapeutically important plant that synthesizes important cardiotonics such as digitoxin and digoxin. The present work reports a detailed and efficient propagation protocol for D. purpurea by optimizing various PGR concentrations in Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium. The genetic homogeneity of in vitro regenerants was assessed by the flow cytometric method (FCM) and Start Codon Targeted (SCoT) marker technique. Firstly, the seeds inoculated in full MS medium added with 0.5 mg/L GA3 produced seedlings. Different parts such as hypocotyl, nodes, leaves and apical shoots were used as explants. The compact calli were obtained on BAP alone or in combinations with 2, 4-D/NAA. The hypocotyl-derived callus induced somatic embryos which proliferated and germinated best in 0.75 mg/L BAP-fortified MS medium. Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) images confirmed the presence of various developmental stages of somatic embryos. Shoot regeneration was obtained in which BAP at 1.0 mg/L and 2.0 mg/L BAP + 0.5 mg/L 2,4-D proved to be the best treatments of PGRs in inducing direct and indirect shoot buds. The regenerated shoots showed the highest rooting percentage (87.5%) with 24.7 ± 1.9 numbers of roots/shoot in 1.0 mg/L IBA augmented medium. The rooted plantlets were acclimatized in a greenhouse at a survival rate of 85-90%. The genome size and the 2C nuclear DNA content of field-grown, somatic embryo-regenerated and organogenic-derived plants were estimated and noted to be 3.1, 3.2 and 3.0 picogram (pg), respectively; there is no alteration in ploidy status and the DNA content, validating genetic uniformity. Six SCoT primers unveiled 94.3%-95.13% monomorphic bands across all the plant samples analyzed, further indicating genetic stability among in vitro clones and mother plants. This study describes for the first time successful induction of somatic embryos from hypocotyl callus; and flow cytometry and SCoT marker confirmed the genetic homogeneity of regenerated plants.
Keywords: SCoT marker; SEM; flow cytometry; genetic homogeneity; indirect somatic embryogenesis; nuclear DNA content; shoot organogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest in the current research investigation.
Figures



References
-
- Patil J.G., Ahire M.L., Nitnaware K.M., Panda S., Bhatt V.P., Kishor P.B.K., Nikam T.D. In Vitro propagation and production of cardiotonic glycosides in shoot cultures of Digitalis purpurea L. by elicitation and precursor feeding. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013;97:2379–2393. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4489-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu B., Li Y., Yan H., Ma Y., Luo H., Yuan L., Chen S., Lu S. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis reveals novel genes involved in cardiac glycoside biosynthesis and mlnc RNAs associated with secondary metabolism and stress response in Digitalis purpurea. BMC Genom. 2012;13:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verma S.K., Das A.K., Cingoz G.S., Gurel E. In Vitro culture of Digitalis L. (Foxglove) and the production of cardenolides: An up-to-date review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016;94:20–51. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.08.031. - DOI
-
- Rad M.M., Abdossi V., Moradi P., Rakhshandehroo F., Mehrafarin A. Phytochemical changes of Digitalis purpurea L. in response to polyamines and methyl jasmonate application in callus culture. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022;31:310–319. doi: 10.1007/s13562-021-00678-w. - DOI
-
- Verma S.K., Sahin G., Yucesan B., Eker I., Sahbaz N., Gurel S., Gurel E. Direct somatic embryogenesis from hypocotyl segments of Digitalis trojana Ivan and subsequent plant regeneration. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012;40:76–80. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.02.034. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

