Influence of Melatonin Treatment on Cellular Mechanisms of Redox Adaptation in K562 Erythroleukemic Cells
- PMID: 36553603
- PMCID: PMC9778059
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122337
Influence of Melatonin Treatment on Cellular Mechanisms of Redox Adaptation in K562 Erythroleukemic Cells
Abstract
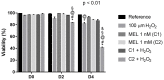
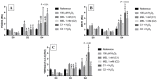
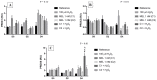
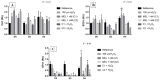
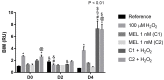
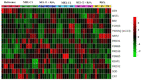
Melatonin (MEL) presents well-documented pleiotropic actions against oxidative stress (OS), acting indirectly through activation of transcription factors, e.g., FoxO3 and Nrf2. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the possible modulating effects of MEL on the redox signaling pathways PI3K/AKT/FoxO3 and Keap1/Nrf2/ARE in K562 erythroleukemic cells subjected to OS induction. For this, the viability, and transcript levels of genes involved in redox adaptation were evaluated in K562 cells in different periods of erythroid differentiation: under OS induction by hydrogen peroxide (100 µM H2O2); treated with 1 nM (C1) and 1 mM (C2) MEL; and associated or not with stress induction. We observed a restoration of physiological levels of Nrf2 in both MEL concentrations under OS. The C1 was related to enhanced expression of antioxidant and proteasome genes through the Nrf2-ARE pathway, while C2 to the induction of FOXO3 expression, suggesting an involvement with apoptotic pathway, according to BIM transcript levels. The effects of MEL administration in these cells showed a period and dose-dependent pattern against induced-OS, with direct and indirect actions through different pathways of cellular adaptation, reinforcing the importance of this indolamine in the regulation of cellular homeostasis, being a promising therapeutic alternative for diseases that present an exacerbated OS.
Keywords: FoxO3; N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]; Nrf2; antioxidant therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
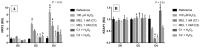
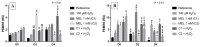
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

