Spotlight on a Short-Time Treatment with the IL-4/IL-13 Receptor Blocker in Patients with CRSwNP: microRNAs Modulations and Preliminary Clinical Evidence
- PMID: 36553635
- PMCID: PMC9777725
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122366
Spotlight on a Short-Time Treatment with the IL-4/IL-13 Receptor Blocker in Patients with CRSwNP: microRNAs Modulations and Preliminary Clinical Evidence
Abstract
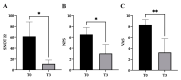
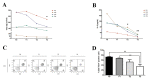
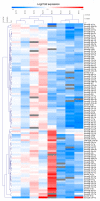
Already used for the treatment of some allergic and inflammatory diseases, such as asthma or atopic dermatitis, dupilumab has also been approved as add-on therapy for patients with CRSwNP, and it could represent the keystone to reducing the remission time as well as to improve healing and quality of life. On the other hand, the role of miRNAs as potential biomarkers of immune modulation is emerging. We analyzed the effects of a short-time treatment with dupilumab in patients with CRSwNP, analyzing the immune response modification as well as miRNAs modulations. First, in this early observation stage, all patients experienced remarkable improvement and were clinically stable. Indeed, we observed a significant decrease in CD4+ T cells and a significant reduction in total IgE (p < 0.05) and serum IL-8 levels (p < 0.01), indicating a reduction in the general inflammatory condition. In addition, we analyzed a panel of about 200 circulating miRNAs. After treatment, we noted a significant downregulation of hsa-mir-25-3p (p-value = 0.02415) and hsa-mir-185-5p (p-value = 0.04547), two miRNAs involved in the proliferation, inflammation, and dug-resistance, in accordance with the clinical status of patients. All these preliminary data aimed to identify new biomarkers of prognosis, identifiable with non-invasive procedures for patients. Further, these patients are still under observation, and others with different levels of responsiveness to treatment need to be enrolled to increase the statistical data.
Keywords: T cells; anti-IL-4/IL-13 receptor; antibody therapeutics; dupilumab; interleukins; miRNAs; nasal polyposis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dupilumab reduces local type 2 pro-inflammatory biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis.Allergy. 2019 Apr;74(4):743-752. doi: 10.1111/all.13685. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 30488542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dupilumab improves upper and lower airway disease control in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and asthma.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021 May;126(5):584-592.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2021.01.012. Epub 2021 Jan 16. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33465455 Clinical Trial.
-
Dupilumab: A Review in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Drugs. 2020 May;80(7):711-717. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01298-9. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32240527 Review.
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: mechanistic insights from targeting IL-4 and IL-13 via IL-4Rα inhibition with dupilumab.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020 Dec;16(12):1115-1125. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1847083. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33148074 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials.Lancet. 2019 Nov 2;394(10209):1638-1650. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31881-1. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31543428 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Preclinical immunological characterization of rademikibart (CBP-201), a next-generation human monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4Rα, for the treatment of Th2 inflammatory diseases.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 31;13(1):12411. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39311-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37524768 Free PMC article.
-
Asthma improvement in patients treated with dupilumab for severe atopic dermatitis.Front Allergy. 2023 Sep 11;4:1223657. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2023.1223657. eCollection 2023. Front Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37753208 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the epigenetics of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps: a systematic review.Front Allergy. 2023 May 22;4:1165271. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2023.1165271. eCollection 2023. Front Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37284022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Individualized Prognostic Model in Patients with Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Serum Metabolomic Profiling.Life (Basel). 2023 May 11;13(5):1167. doi: 10.3390/life13051167. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240811 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in CRSwNP: The Role of MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 10;47(2):114. doi: 10.3390/cimb47020114. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39996835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jonstam K., Swanson B.N., Mannent L.P., Cardell L., Tian N., Wang Y., Zhang D., Fan C., Holtappels G., Hamilton J.D., et al. Dupilumab reduces local type 2 pro-inflammatory biomarkers in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Allergy. 2019;74:743–752. doi: 10.1111/all.13685. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

