Dual Molecular Diagnoses of Recessive Disorders in a Child from Consanguineous Parents: Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 36553645
- PMCID: PMC9778442
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122377
Dual Molecular Diagnoses of Recessive Disorders in a Child from Consanguineous Parents: Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
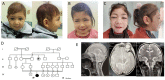
The widespread use of whole exome sequencing (WES) resulted in the discovery of multilocus pathogenic variations (MPV), defined as two or more distinct or overlapping Mendelian disorders occurring in a patient, leading to a blended phenotype. In this study, we report on a child with autosomal recessive primary microcephaly-5 (MCPH5) and nephropathic cystinosis. The proband is the first child of consanguineous parents, presenting a complex phenotype including neurodevelopmental delay, microcephaly, growth restriction, significant delay of bone maturation, lissencephaly, and abnormality of neuronal migration, photophobia, and renal tubular acidosis. WES revealed two pathogenic and homozygous variants: a c.4174C>T variant in the ASPM gene and a c.382C>T variant in the CTNS gene, explaining the complex phenotype. The literature review showed that most of the patients harboring two variants in recessive disease genes are born to consanguineous parents. To the best of our knowledge, the patient herein described is the first one harboring pathogenic variants in both the ASPM and CTNS genes. These findings highlight the importance of searching for MPV in patients with complex phenotypes investigated by genome-wide testing methods, especially for those patients born to consanguineous parents.
Keywords: ASPM; CTNS; consanguineous parents; dual molecular diagnoses; nephropathic cystinosis; primary microcephaly; recessive inheritance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Herman I., Jolly A., Du H., Dawood M., Abdel-Salam G.M.H., Marafi D., Mitani T., Calame D.G., Coban-Akdemir Z., Fatih J.M., et al. Quantitative dissection of multilocus pathogenic variation in an Egyptian infant with severe neurodevelopmental disorder resulting from multiple molecular diagnoses. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2022;188:735–750. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62565. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith E.D., Blanco K., Sajan S.A., Hunter J.M., Shinde D.N., Wayburn B., Rossi M., Huang J., Stevens C.A., Muss C., et al. A retrospective review of multiple findings in diagnostic exome sequencing: Half are distinct and half are overlapping diagnoses. Genet. Med. 2019;21:2199–2207. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0477-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

