Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: Current Techniques, Applications, and Role in COVID-19 Diagnosis
- PMID: 36553654
- PMCID: PMC9778061
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122387
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: Current Techniques, Applications, and Role in COVID-19 Diagnosis
Abstract
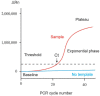
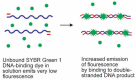
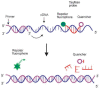
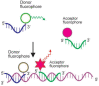
Successful detection of the first SARS-CoV-2 cases using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) method reflects the power and usefulness of this technique. Real-time PCR is a variation of the PCR assay to allow monitoring of the PCR progress in actual time. PCR itself is a molecular process used to enzymatically synthesize copies in multiple amounts of a selected DNA region for various purposes. Real-time PCR is currently one of the most powerful molecular approaches and is widely used in biological sciences and medicine because it is quantitative, accurate, sensitive, and rapid. Current applications of real-time PCR include gene expression analysis, mutation detection, detection and quantification of pathogens, detection of genetically modified organisms, detection of allergens, monitoring of microbial degradation, species identification, and determination of parasite fitness. The technique has been used as a gold standard for COVID-19 diagnosis. Modifications of the standard real-time PCR methods have also been developed for particular applications. This review aims to provide an overview of the current applications of the real-time PCR technique, including its role in detecting emerging viruses such as SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; molecular diagnosis; polymerase chain reaction; quantitative PCR; real-time PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel dual multiplex real-time RT-PCR assays for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2, influenza A/B, and respiratory syncytial virus using the BD MAX open system.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):161-166. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1873073. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 33410371 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction-Free Rapid Cycle Quantitative RT-PCR and Extreme RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 Virus Detection.J Mol Diagn. 2021 Dec;23(12):1671-1679. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2021.08.004. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Mol Diagn. 2021. PMID: 34454108 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Aspects Concerning the Development of a Pooling Approach for SARS-CoV-2 Diagnosis Using Large-Scale PCR Testing.Viruses. 2021 May 13;13(5):902. doi: 10.3390/v13050902. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34067983 Free PMC article.
-
Detection profile of SARS-CoV-2 using RT-PCR in different types of clinical specimens: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2021 Feb;93(2):719-725. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26349. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32706393 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances and challenges of RT-PCR tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 May;221:153443. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153443. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33930607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Recombinase Polymerase Amplification: Methods for Quick and Cost-Effective Detection of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE).Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Mar 12;14(3):295. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14030295. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149105 Free PMC article.
-
Biocides as drivers of antibiotic resistance: A critical review of environmental implications and public health risks.Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2025 Mar 24;25:100557. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2025.100557. eCollection 2025 May. Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40230384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visfatin Facilitates VEGF-D-Induced Lymphangiogenesis through Activating HIF-1α and Suppressing miR-2277-3p in Human Chondrosarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5142. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105142. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791180 Free PMC article.
-
Brief guide to RT-qPCR.Mol Cells. 2024 Dec;47(12):100141. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100141. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Mol Cells. 2024. PMID: 39476972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific detection of pigeon parvovirus with TaqMan real-time PCR technology.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104541. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104541. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39603190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sucahya P.K. Barriers to COVID-19 RT-PCR testing in Indonesia: A health policy perspective. J. Indones. Health Policy Admin. 2020;5:36–42. doi: 10.7454/ihpa.v5i2.3888. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

