Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group's Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean
- PMID: 36553683
- PMCID: PMC9777564
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13122417
Population Genetics and Anastomosis Group's Geographical Distribution of Rhizoctonia solani Associated with Soybean
Abstract
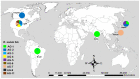
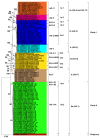
Rhizoctonia solani is a species complex composed of many genetically diverse anastomosis groups (AG) and their subgroups. It causes economically important diseases of soybean worldwide. However, the global genetic diversity and distribution of R. solani AG associated with soybean are unknown to date. In this study, the global genetic diversity and distribution of AG associated with soybean were investigated based on rDNA-ITS sequences deposited in GenBank and published literature. The most prevalent AG, was AG-1 (40%), followed by AG-2 (19.13%), AG-4 (11.30%), AG-7 (10.43%), AG-11 (8.70%), AG-3 (5.22%) and AG-5 (3.48%). Most of the AG were reported from the USA and Brazil. Sequence analysis of internal transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA separated AG associated with soybean into two distinct clades. Clade I corresponded to distinct subclades containing AG-2, AG-3, AG-5, AG-7 and AG-11. Clade II corresponded to subclades of AG-1 subgroups. Furthermore, AG and/or AG subgroups were in close proximity without corresponding to their geographical origin. Moreover, AG or AG subgroups within clade or subclades shared higher percentages of sequence similarities. The principal coordinate analysis also supported the phylogenetic and genetic diversity analyses. In conclusion, AG-1, AG-2, and AG-4 were the most prevalent AG in soybean. The clade or subclades corresponded to AG or AG subgroups and did not correspond to the AG's geographical origin. The information on global genetic diversity and distribution will be helpful if novel management measures are to be developed against soybean diseases caused by R. solani.
Keywords: R. solani; anastomosis groups; distribution; genetic diversity; phylogeny; soybean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unveiling the Genetic Tapestry: Exploring Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 Anastomosis Groups in Potato Crops across Borders.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 3;13(5):715. doi: 10.3390/plants13050715. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475561 Free PMC article.
-
Biological characteristics and metabolic phenotypes of different anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani strains.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jun 20;24(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03363-9. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38902632 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy for Gaucher's disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jul;10(24):iii-iv, ix-136. doi: 10.3310/hta10240. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16796930
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
Cited by
-
Advancing fungal phylogenetics: integrating modern sequencing, dark taxa discovery, and machine learning.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Jul 11;207(9):192. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04392-2. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40643763 Review.
-
Unveiling the Genetic Tapestry: Exploring Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 Anastomosis Groups in Potato Crops across Borders.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 3;13(5):715. doi: 10.3390/plants13050715. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475561 Free PMC article.
-
Leguminous Seedborne Pathogens: Seed Health and Sustainable Crop Management.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 19;12(10):2040. doi: 10.3390/plants12102040. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Surbhi K., Singh K.P., Singh N.K., Aravind T. Assessment of genetic diversity among soybean genotypes differing in response to aerial blight (Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn) using SSR markers. J. Phytopathol. 2021;169:37–44. doi: 10.1111/jph.12956. - DOI
-
- Lewandowska S., Łoziński M., Marczewski K., Kozak M., Schmidtke K. Influence of priming on germination, development, and yield of soybean varieties. Open Agric. 2020;5:930–935. doi: 10.1515/opag-2020-0092. - DOI
-
- Ajayi-Oyetunde O., Bradley C. Rhizoctonia solani: taxonomy, population biology and management of Rhizoctonia seedling disease of soybean. Plant pathol. 2018;67:3–17. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12733. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

