Microbiological and Sensorial Quality of Beef Meat (Longissimus dorsi) Marinated with Cinnamon Extract and Stored at Various Temperatures
- PMID: 36553712
- PMCID: PMC9778215
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11243971
Microbiological and Sensorial Quality of Beef Meat (Longissimus dorsi) Marinated with Cinnamon Extract and Stored at Various Temperatures
Abstract
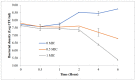
Meat spoilage caused by temperature abuse is a major problem for producers, retailers, and consumers that can generate large economic losses to industries. Microbial growth of Pseudomonas spp. is the main source of spoilage during storage. Cinnamon has antimicrobial properties that may potentially be used to reduce the spoilage caused by Pseudomonas. The objectives of this study were to determine the inhibitory effect of cinnamon extract (CE) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 27853) and evaluate the treatment of CE on meat quality during different storage temperatures (5 °C, 10 °C, 15 °C, and 25 °C). The anti-Pseudomonas result showed that 100% (w/v) CE concentration produced a 13.50 mm zone of inhibition in a disc diffusion assay. The minimum inhibitor concentration (MIC) of CE was noted at 25% (v/v), whereas the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) value was observed at 50% (v/v) concentration of CE. The time-kill showed the growth of P. aeruginosa decreased from 7.64 to 5.39 log CFU/mL at MIC concentration. Total phenolic content and IC50 value of the cinnamon extract was expressed as 6.72 ± 0.87 mg GAE/g extract and 0.15 mg/mL, respectively. When the meat was marinated with 50% (v/v) CE and stored at various temperatures, the total viable count (TVC) and growth of Pseudomonas spp. were lowered as compared to the control sample. However, the reduction in microbial count in all samples was influenced by the storage temperature, where the lowered microbial count was noted in the sample treated with CE and stored at 5 and 10 °C for 48 h. The pH of meat treated with or without CE ranged from pH 5.74 to 6.48. The sensory attributes of colour, texture, and overall acceptability have a significant difference, except for odour, between marinated meat and control. The results indicate that the use of cinnamon extract as the marination agent for meat could reduce the growth of Pseudomonas spp. and therefore assist in extending the shelf life of meat at 5 and 10 °C storage temperatures.
Keywords: Pseudomonas spp.; antimicrobial; antioxidant; cinnamon extract; meat; shelf-life extension; storage temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined effects of thymol, carvacrol and packaging on the shelf-life of marinated chicken.Int J Food Microbiol. 2019 Feb 16;291:42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Int J Food Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30445284
-
Effect of pomegranate based marinades on the microbiological, chemical and sensory quality of chicken meat: A metabolomics approach.Int J Food Microbiol. 2018 Feb 21;267:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.12.023. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Int J Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29288907
-
Efficacies of soy sauce and wine base marinades for controlling spoilage of raw beef.Food Microbiol. 2011 Feb;28(1):158-63. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2010.09.013. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Food Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21056788
-
Synergistic effect of spice extracts and modified atmospheric packaging towards non-thermal preservation of chicken meat under refrigerated storage.Poult Sci. 2017 Aug 1;96(8):2839-2844. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex057. Poult Sci. 2017. PMID: 28520947
-
Antimicrobial effect of thymol and carvacrol added to a vinegar-based marinade for controlling spoilage of marinated beef (Shawarma) stored in air or vacuum packaging.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Nov 2;332:108769. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108769. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32622249
Cited by
-
Effects of UV-C Irradiation and Vacuum Sealing on the Shelf-Life of Beef, Chicken and Salmon Fillets.Foods. 2023 Feb 1;12(3):606. doi: 10.3390/foods12030606. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36766135 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Epigallocatechin Gallate-Enriched Antioxidant Edible Films Based on Konjac Glucomannan and Sodium Alginate: Impact on Storage Stability of Mandarin Fish.Foods. 2025 Apr 29;14(9):1570. doi: 10.3390/foods14091570. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361650 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Sesame and Cinnamon extract on physicochemical characteristics, oxidative stability, and antimicrobial activity in fresh poultry meatballs at refrigerated storage.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul 13;104(10):105572. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105572. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40752202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogataj D., Hudoklin D., Bogataj M., Dimovski V., Colnar S. Risk mitigation in a meat supply chain with options of redirection. Sustainability. 2020;12:8690. doi: 10.3390/su12208690. - DOI
-
- Ndraha N., Hsiao H.I., Vlajic J., Yang M.F., Lin H.T.V. Time-temperature abuse in the food cold chain: Review of issues, challenges, and recommendations. Food Control. 2018;89:12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.01.027. - DOI
-
- Koutsoumanis K., Stamatiou A., Skandamis P., Nychas G.-J.E. Development of a microbial model for the combined effect of temperature and pH on spoilage of ground meat and validation of the model under dynamic temperature conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006;72:124–134. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.124-134.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous