Effect and Correlation of Rosa roxburghii Tratt Fruit Vinegar on Obesity, Dyslipidemia and Intestinal Microbiota Disorder in High-Fat Diet Mice
- PMID: 36553852
- PMCID: PMC9778257
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11244108
Effect and Correlation of Rosa roxburghii Tratt Fruit Vinegar on Obesity, Dyslipidemia and Intestinal Microbiota Disorder in High-Fat Diet Mice
Abstract
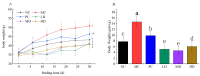
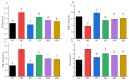
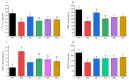
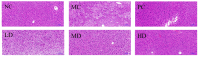
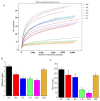
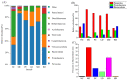
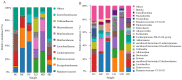
To investigate the effect of Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit vinegar (RFV) on the intervention of obesity and hyperlipidemia and its potential mechanism, a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity model in mice was established and gavaged with RFV, saline and xuezhikang for 30 consecutive days, respectively. The results showed that RFV supplementation significantly reduced fat accumulation, and improved dyslipidemia and liver inflammation in HFD mice. RFV intervention for 30 days significantly improved the diversity of gut microbiota and altered the structure of gut microbiota in HFD mice. Compared with the model group (MC), the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes at least decreased by 15.75% after RFV treatment, and increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria (Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Lactobacillaceae, Bacteroides, Akkermansia,) and decreased the relative abundance of harmful bacteria (Ruminococcaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae, Ruminococcaceae _UCG-013, Lachnospiraceae, Allobaculum, Actinobacteria). Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that Erysipelotrichaceae, Allobaculum, Lachnospiraceae, Ruminococcaceae, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-013, uncultured_bacterium_f_Lachnospiraceae and Desulfobacterota were positively correlated (p < 0.05) with the body weight of mice, while Proteobacteria was negatively correlated (p < 0.05) with the body weight of mice. The two main bacteria that could promote dyslipidemia in obese mice were Actinobacteria and Firmicutes, while those that played a mitigating role were mainly Bacteroidetes. It is concluded that RFV plays an important role in the intervention of obesity and related complications in HFD mice by regulating their gut microbiota.
Keywords: Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit vinegar; correlation; dyslipidemia; gut microbiota regulation; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect and Correlation of Rosa roxburghii Tratt Juice Fermented by Lactobacillus paracasei SR10-1 on Oxidative Stress and Gut Microflora Dysbiosis in Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice.Foods. 2023 Aug 28;12(17):3233. doi: 10.3390/foods12173233. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37685166 Free PMC article.
-
Prebiotic properties of the polysaccharide from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit and its protective effects in high-fat diet-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction: A fecal microbiota transplantation study.Food Res Int. 2023 Feb;164:112400. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112400. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36737985
-
A polysaccharide from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit attenuates high-fat diet-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation in mice by modulating the gut microbiota.Food Funct. 2022 Jan 24;13(2):530-547. doi: 10.1039/d1fo03190b. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 34932054
-
Pu-erh tea ameliorates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high fat diet fed mice.Food Res Int. 2021 Jun;144:110360. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110360. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34053553
-
The role of gut microbiota on cognitive development in rodents: a meta-analysis.J Physiol Sci. 2023 May 16;73(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12576-023-00869-1. J Physiol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37193943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the mechanism of jujube vinegar on hyperlipoidemia through gut microbiome based on 16S rRNA, BugBase analysis, and the stamp analysis of KEEG.Front Nutr. 2023 May 19;10:1160069. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1160069. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37275638 Free PMC article.
-
Effect and Correlation of Rosa roxburghii Tratt Juice Fermented by Lactobacillus paracasei SR10-1 on Oxidative Stress and Gut Microflora Dysbiosis in Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice.Foods. 2023 Aug 28;12(17):3233. doi: 10.3390/foods12173233. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37685166 Free PMC article.
-
Rosa Roxburghii Tratt Fruit Extract Prevents Dss-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and the IL-17 Signaling Pathway.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 27;15(21):4560. doi: 10.3390/nu15214560. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960213 Free PMC article.
-
Rosa roxburghii Tratt juice inhibits NF-κB and increases IL-2 to alleviates the Foxp3-mediated Tregs imbalance in the peripheral blood of arseniasis patients.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 24;33(4):935-944. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01384-0. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38371687 Free PMC article.
-
Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit extract ameliorate free fatty acid induced steatosis in HepG2 cells through activating PI3K-Akt and PPAR pathways.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 18;15(1):26169. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12126-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40681729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He J., Zhang Y., Ma N., Zhang X., Liu M., Fu W. Comparative analysis of multiple ingredients in Rosa roxburghii and R. sterilis fruits and their antioxidant activities. J. Funct. Foods. 2016;27:29–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.08.058. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

