Analysing Researchers' Engagement in Research Hospitals: A Pilot Study in IRCCS-Italian Research Hospitals
- PMID: 36553982
- PMCID: PMC9778415
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10122458
Analysing Researchers' Engagement in Research Hospitals: A Pilot Study in IRCCS-Italian Research Hospitals
Abstract
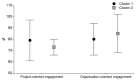
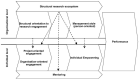
Despite universities in the UK, USA and Australia having developed tools and strategies to enhance academic engagement, there is a paucity of information from universities and research hospitals where conceptual and theoretical research still appears more heterogeneous. In Italy, there is a growing recognition that more needs to be done to define strategies to improve research engagement. Italian research hospitals are represented by the Scientific Institute for Research, Hospitalization and Healthcare (named IRCCS from the Italian acronym of these organisations), representing the best of Italian research and the National Health Service System. This article provided a pilot description of research engagement in a representative Italian IRCCS hospital for the first time. A pilot study was developed, and a brief questionnaire was validated to explore research engagement. The identified clusters of researchers' engagement were provided to describe an initial theory-grounded framework. Based on the perspective of research administrators and the Ministry of Health during round tables, the developed questionnaire identified two clusters of researchers' engagement and measured "Project-oriented" and "Organisation-oriented" engagement. Among the responders, IRCCS senior researchers tended to have higher project-oriented engagement, while young researchers had slightly higher organisation-oriented engagement. The contribution of this article is a hypothesised two-level theory-grounded framework to study and improve research engagement activities and strategies in a research hospital, with the potential for an overlap with other European research institutions.
Keywords: organisation science; qualitative methods; research engagement; research hospitals; surveys.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Scott J.C. The Mission of the University: Medieval to Postmodern Transformations. J. High. Educ. 2006;77:1–39. doi: 10.1353/jhe.2006.0007. - DOI
-
- Perkmann M., Tartari V., McKelvey M., Autio E., Broström A., D’Este P., Fini R., Geuna A., Grimaldi R., Hughes A., et al. Academic Engagement and Commercialisation: A Review of the Literature on University-Industry Relations. Res. Policy. 2013;42:423–442. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2012.09.007. - DOI
-
- Giusepponi K., Tavoletti E. Vision and Mission Statements in Italian Universities: Results of an Empirical Investigation on Strategic Orientation. J. Knowl. Econ. 2018;9:301–328. doi: 10.1007/s13132-015-0343-7. - DOI
-
- Consoli D., Mina A. An Evolutionary Perspective on Health Innovation Systems. J. Evol. Econ. 2008;19:297–319. doi: 10.1007/s00191-008-0127-3. - DOI
-
- Djellal F., Gallouj F., Clersé F.G. Mapping Innovation Dynamics in Hospitals. Res. Policy. 2005;34:817–835. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2005.04.007. - DOI

