Severe Recurrent COVID-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Challenging Case
- PMID: 36554008
- PMCID: PMC9778552
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10122483
Severe Recurrent COVID-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Challenging Case
Abstract
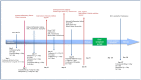
We report a rare case of severe COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis presenting as invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and subsequently invasive tracheobronchial aspergillosis during hospitalization in a critically ill patient who developed a further Aspergillus infection after home discharge. He needed readmission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation. We therefore strongly encourage a high degree of attention to fungal complications, even after viral recovery and ICU discharge.
Keywords: COVID-19; critically ill patient; mechanical ventilation; pulmonary aspergillosis; tracheostomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lung epithelial and myeloid innate immunity in influenza-associated or COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: an observational study.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Dec;10(12):1147-1159. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00259-4. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 36029799 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological diagnosis of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: a bronchoalveolar study.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023 Oct 10;22(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12941-023-00626-7. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023. PMID: 37817167 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive Tracheobronchial Aspergillosis in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Influenza. A Clinical Trial.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Sep 1;202(5):708-716. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201910-1931OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32407157
-
Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Review of definitions and diagnostic approaches.Mycoses. 2021 Sep;64(9):1002-1014. doi: 10.1111/myc.13274. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 33760284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point-of-care testing for viral-associated pulmonary aspergillosis.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024 Mar;24(3):231-243. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2023.2257597. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024. PMID: 37688631 Review.
Cited by
-
Typing of Candida spp. from Colonized COVID-19 Patients Reveal Virulent Genetic Backgrounds and Clonal Dispersion.Pathogens. 2023 Sep 29;12(10):1206. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101206. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37887722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamam J., Navellou J.-C., Bellanger A.-P., Bretagne S., Winiszewski H., Scherer E., Piton G., Millon L., Collaborative RESSIF Group New clinical algorithm including fungal biomarkers to better diagnose probable invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU. Ann. Intensive Care. 2021;11:41. doi: 10.1186/s13613-021-00827-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verweij P.E., Rijnders B.J.A., Brüggemann R.J.M., Azoulay E., Bassetti M., Blot S., Calandra T., Clancy C.J., Cornely O.A., Chiller T., et al. Review of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients and proposal for a case definition: An expert opinion. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:1524–1535. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06091-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartoletti M., Pascale R., Cricca M., Rinaldi M., Maccaro A., Bussini L., Fornaro G., Tonetti T., Pizzilli G., Francalanci E., et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Among Intubated Patients With COVID-19: A Prospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020;73:e3606–e3614. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1065. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

