Study and Application of Urban Aquatic Ecosystem Health Evaluation Index System in River Network Plain Area
- PMID: 36554433
- PMCID: PMC9779142
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192416545
Study and Application of Urban Aquatic Ecosystem Health Evaluation Index System in River Network Plain Area
Abstract
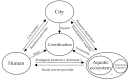
The evaluation index system of urban aquatic ecosystem health is of great significance for the assessment and management of urban river networks, and for urban development planning. In this paper, the concept of urban aquatic ecosystem health was analyzed by the relationship between human, city and aquatic ecosystem, and its evaluation index system was established from environmental conditions, ecological construction, and social service. In addition, the weight value of each index was calculated by the analytic hierarchy process, and the grading standard of each index was set. Jiading New City, a typical city of the river network plain area in Yangtze River delta, was selected as the aquatic ecosystem health evaluation sample. The fuzzy comprehensive method was used to evaluate the aquatic ecosystem health of Jiading New City. The results indicated that the water ecosystem health of Jiading New City reached the "good" level. For the criterion level, environmental conditions and ecological construction reached the "good" level, and social services reached the "excellent" level. For the indicator level, most indicators reached "good" and "excellent" levels, but the river complexity and benthic macroinvertebrate diversity are still in the "poor" state, which indicates that the aquatic environment has greatly improved, but the aquatic ecosystem has not been fully restored. Results suggested that river complexity and biodiversity should be increased in urban construction planning. The evaluation index system established in this paper can be used to reflect the urban aquatic ecosystem health conditions in river network plain areas.
Keywords: analytic hierarchy process; evaluation index system; fuzzy comprehensive evaluation; river network plain area; urban aquatic ecosystem health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Response of macroinvertebrate community to water quality factors and aquatic ecosystem health assessment in a typical river in Beijing, China.Environ Res. 2022 Sep;212(Pt D):113474. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113474. Epub 2022 May 17. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35594960
-
Establishment and Application of the Assessment System on Ecosystem Health for Restored Urban Rivers in North China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 5;19(9):5619. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095619. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35565007 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for the assessment of urban stream health in Jinan City, China.Environ Monit Assess. 2017 May;189(5):205. doi: 10.1007/s10661-017-5920-8. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Environ Monit Assess. 2017. PMID: 28374188
-
[Quantitative Analysis of the Correlation Between Macrobenthos Community and Water Environmental Factors and Aquatic Ecosystem Health Assessment in the North Canal River Basin of Beijing].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022 Jan 8;43(1):247-255. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202104158. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022. PMID: 34989509 Chinese.
-
[Relationship Between Macrophyte Communities and Macroinvertebrate Communities in an Urban Stream].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2018 Feb 8;39(2):783-791. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201708082. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2018. PMID: 29964842 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Assessment of potential dominant factors for brownfield landscape regeneration: A case study in Xi'an, China.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 10;20(2):e0312668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312668. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39928680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Su Y., Li W., Liu L., Hu W., Li J., Sun X., Li Y. Health assessment of small-to-medium sized rivers: Comparison between comprehensive indicator method and biological monitoring method. Ecol. Indic. 2021;126:107686. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107686. - DOI
-
- Moiwo J.P., Yang Y., Li H., Han S., Yang Y. Impact of water resource exploitation on the hydrology and water storage in Baiyangdian Lake. Hydrol. Process. 2010;24:3026–3039. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7716. - DOI
-
- Kavzolu T. Determination of environmental degradation due to urbanization and industrialization in Gebze, Turkey. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008;25:429–438. doi: 10.1089/ees.2006.0271. - DOI
-
- Hale R., Coleman R., Pettigrove V., Swearer S.E. Identifying, preventing and mitigating ecological traps to improve the management of urban aquatic ecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015;52:928–939. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12458. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources